 |
 |
| Plant Pathol J > Volume 38(2); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum (Pcc) is a gram-negative, broad host range bacterial pathogen which causes soft rot disease in potatoes as well as other vegetables worldwide. While Pectobacterium infection relies on the production of major cell wall degrading enzymes, other virulence factors and the mechanism of genetic adaptation of this pathogen is not yet clear. In the present study, we have performed an in-depth genome-wide characterization of Pcc strain ICMP5702 isolated from potato and compared it with other pathogenic bacteria from the Pectobacterium genus to identify key virulent determinants. The draft genome of Pcc ICMP5702 contains 4,774,457 bp with a G + C content of 51.90% and 4,520 open reading frames. Genome annotation revealed prominent genes encoding key virulence factors such as plant cell wall degrading enzymes, flagella-based motility, phage proteins, cell membrane structures, and secretion systems. Whereas, a majority of determinants were conserved among the Pectobacterium strains, few notable genes encoding AvrE-family type III secretion system effectors, pectate lyase and metalloprotease in addition to the CRISPR-Cas based adaptive immune system were uniquely represented. Overall, the information generated through this study will contribute to decipher the mechanism of infection and adaptive immunity in Pcc.
The bacterial genus Pectobacterium (formerly classified as the Erwinia genus) is a group of facultative anaerobic, gram-negative, non-sporulating, motile bacteria belonging to the Pectobacteriaceae family. The Pectobacterium genus is heterogeneous and at the time writing, has 17 species (P. carotovorum, P. cacticida, P. betavasculorum, P. wasabiae, P. aroidearum, P. peruviense, P. parmentieri, P. polaris, P. atrosepticum, P. rhapontici, P. cypropedi, P. carnegieana, P. odoriferum, P. brasiliense, P. actnidiae, P. aquaticum, and P. versatile) (Li et al., 2019; Nykyri et al., 2012; Portier et al., 2019). Many of these species were identified as strains of P. carotovorum and subsequently been elevated as new species including P. odoriferum, P. brasiliense, and P. actnidiae (Portier et al., 2019). Most notably, the Candidatus P. maceratum has been renamed as P. versatile owing to the generic nature of themetabolic feature common to all pectinolytic bacteria and not suitable for description of a single clade (Portier et al., 2019). While P. parmentieri, P. carotovorum, and P. atrosepticum causes the most severe soft rot infections, P. parmentieri and P. atrosepticum are largely host specific. In contrast, P. carotovorum which is the causal agent of the potato soft rot disease is the most devastating pathogen with the widest host range among all of the soft rot bacteria (Davidsson et al., 2013). P. carotovorum is characterized by the presence of a wide range of pathogenicity determinants to facilitate maceration associated diseases. Hence, it is considered as a model pathogen to elucidate the genetic basis of bacterial phytpathogenity. Therefore, the development of effective strategies to protect crops from soft rot disease demands comprehensive understanding of the the pathogenic taxonomy and molecular basis of host-pathogen interactions.
The symptoms caused by Pectobacterium infection include water-soaked lesions which lead to collapse of the infected tissue, wilting and death of the plants from vascular invasion. Extensive studies on the Pectobacterium pathogens have led to the identification of a number of virulence factors including plant cell wall degradative enzymes (PCWDEs), diverse regulatory systems, and bacterial secretion systems, which cumulatively contribute to the bacterial infections (Toth et al., 2003). The type II secretion system (T2SS) is responsible for the secretion of PCWDEs such as polygalacturonase (Peh), pectate lyase (Pel), cellulase (Cel), xylanase, protease (Prt) which catalyse the breakdown of pectin, the primary plant cell wall component and macerate the plant host tissue during the infection process (Mashavha, 2013). The production of these extracellular enzymes is regulated by two quorum sensing systems-the ExpI/ExpR system and autoinducer-2 dependent signalling systems in P. carotovorum (Crépin et al., 2012). Likewise, the type III secretion system (T3SS), commonly referred to as injectosome, is found in many gram-negative bacterial pathogens, which is a multi-protein complex bacterial structure used to deliver virulent effector proteins directly into host cells (Coburn et al., 2007). A functional T3SS is required for expression of several genes in P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum (Pcc), including the virulence factor gene for pectate lyase (pelB). P. carotovorum uses the T3SS early in leaf infection to initiate pathogenesis through elicitation of DspE mediated host cell response in Solanum tuberosum (Hogan et al., 2013). Fascinatingly, some of the P. carotovorum strains deficient with T3SS also exhibit significant pathogenesis in planta as compared to the T3SS encoding strains. For instance, the virulence of strains of P. carotovorum and P. wasabiae which have multiple deletions within the loci encoding T3SS was found analogous with the T3SS encoding strains in both stems and tubers of potato (Kim et al., 2009). In another study, mutations in the T3SS regulatory and structural genes including the dspE/F operon is unable to induce hypersensitive response including cell death and/or leaf maceration and could not prevent callose deposition (Kim et al., 2011). This suggests that, P. carotovorum utilize the T3SS effectors not to suppress plant immunity but to facilitate cell death and promote leaf maceration.
The cellular regulatory network controls the expression of virulence factors. In the genus Pectobacterium, there are three major, coupled and partly overlapping regulatory systems: The repressor protein, KdgR, which suppresses the production of PCWDEs without induction by host-related immunity, the second pathway involves the widespread quorum sensing system that suppresses production of virulence factors before high population densities are reached within a plant host and the flagellar master regulator, FlhDC which promotes the production of both flagella and PCWDEs (Kõiv et al., 2013). The effect of different cellular and environmental signals is integrated by regulators give rise to a response. Most effector function in P. carotovorum is yet to be determined.
Other than PCWDEs and effectors, the virulence determinants identified in Pectobacterium include cell membrane structures such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), bacteriocins, necrosis-inducing protein, a plant ferredoxin-like protein (FerE) and citrate uptake, and TolC (Lee et al., 2013; Toth et al., 2003). In addition to these determinants, Pectobacterium species also produce small molecules that contribute to virulence. These include siderophores involved in iron acquisition under iron limiting conditions, and various other small molecules that regulate key virulence genes (Charkowski, 2018). The Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats-Cas bacterial defence systems and genome-level variations can also influence the pathogenicity of Pectobacterium (Vercoe et al., 2013). Prophages can increase the virulence potential of bacterial strains in both humans and plant pathogens as well as increase the ability of the bacteria to survive in harsh environments. Comparative genomics study of P. carotovorum and other closely related species have revealed that the core pathogenicity factors are highly conserved in different Pectobacterium species.
Earlier, the draft genome of a type strain of P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum namely ICMP 5702 (GenBank accession no. AODT01000000), the causative agent of soft rot in Solanum tuberosum was sequenced and annotated for important genetic factors. However, no phylogenomic studies were undertaken to ascertain to ascertain their role in potato infection. With rapid improvement in bioinformatics tools, it is now imperative to update the available resources and further confirm the genomic features in the draft genomes of agriculturally important microorganisms like the potato soft rot pathogen (Salzberg, 2019). Keeping this in mind, it was rationale to re-annotate the draft genome sequence of Pcc ICMP 5702. In the present study, we report the genome re-annotation, bioinformatic based characterization of genetic features and phylogenomic analysis of the Pcc ICMP 5702. We also identified an additional 411 functional genes encoding T2SS effectors, T3SS effectors and PCWDE and other pathogenicity-related factors which will be useful for understanding the molecular mechanism of soft rot bacteria and potato interactions. In addition, we also compared the re-annotated genome of Pcc ICMP 570 with the re-annotated genomes of five other P. carotovorum subspecies: Pcc S1, Pcc WPP14, Pcc 21, P. carotovorum subsp. brasiliense (Pcb) SX309, and P. carotovorum subsp. odoriferum (Pco) BCS7 with respect to phylogenetic analyses, general genomic properties and genome similarities.
The raw reads data of the draft genome of Pcc ICMP 5702 (GenBank accession no. AODT01000000) was downloaded from European Nucleotide Archive (ENA). The genome was assembled using the SPAdes (v 3.6.2) tool in Unicycler (Wick et al., 2017). It is a De Bruign graph based assembly tool which removes contigs that has depth of less than half of the median graph depth thereby increasing the accuracy of the assembly. The assembled genome was analyzed for genome size, total number of contigs, average sequence length, N50 value, A + T and G + C percentage using the NGS QC Toolkit. The tandem repeats were predicted with Tandem Repeat Finder (TRF) web server (https://tandem.bu.edu/trf/trf.html) (Benson, 1999).
Protein coding sequences (CDS) and their function were predicted using the RAST Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline (RAST) (https://rast.nmpdr.org/) (Aziz et al., 2008), PANNZER Rapid Functional Annotation Server (http://ekhidna2.biocenter.helsinki.fi/sanspanz/) (Törönen et al., 2018), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes database (KEGG) (https://www.genome.jp/kegg/pathway.html) (Kanehisa et al., 2004), and EggNog databases (http://eggnog5.embl.de/#/app/home) (Huerta-Cepas et al., 2019). PlasmidFinder Web tool was used to identify plasmid replicons in the genome (https://cge.cbs.dtu.dk/services/PlasmidFinder/) (Carattoli et al., 2014). The prophage sequences were identified and annotated by PHASTER (https://phaster.ca/) (Arndt et al., 2016). Putative signal peptides and transmembrane helices were predicted using SignalP 5.0 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/) (Almagro Armenteros et al., 2019) and TMHMM 2.0 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/) (Krogh et al., 2001), respectively. Prediction of virulent proteins was done by VirulentPred web tool (http://203.92.44.117/virulent/index.html) (Garg and Gupta, 2008). The antibiotic resistant genes present in the genome were predicted by the resistance gene finder tool of Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database (CARD) (https://card.mcmaster.ca/analyze/rgi) (Alcock et al., 2020). The 16S rRNA sequence of P. carotovorum ICMP 5702 obtained through Barrnap was used as a query to search against the 16s rRNA database of National Centre for Biotechnology Information (NCBI, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/refseq/targetedloci/16S_process/) by using BLASTn to identify the nearest reference genome. Finally, the Genome FASTA file of ICMP 5702 was uploaded into the CRISPR-Finder server to detect the CRISPR loci (E-value ≤ 0.001) (https://crisprcas.i2bc.paris-saclay.fr/) (Couvin et al., 2018).
The complete genome of related species or subspecies including Pcc 21 (accession: CP003776), Pcc WPP 14 (accession no. CP051652), Pcc S1, Pcb SX309 (accession no. CP020350), and Pco BCS7 (accession no. CP009678) was downloaded from ENA. Average nucleotide identities (ANI) values were computed using ANI calculator webserver (http://enve-omics.ce.gatech.edu/ani/) (Rodriguez and Konstantinidis, 2016). In silico DNA-DNA hybridization (DDH) was determined using the Genome-to-Genome distance calculator webserver (GGDC) (http://ggdc.dsmz.de/ggdc.php#) (Auch et al., 2010). Complete genome comparisons were conducted using the progressive alignment option of the Mauve 2.3.1 comparison software (Darling et al., 2004) with ICMP 5702 as the reference genome. The protein sequence in FASTA format were provided to Orthovenn2 web server as input with default parameter (e-value 1e-5 and inflation value of 1.5) and an interactive Venn diagram showing the clusters of orthologous genes shared between the species was obtained (https://orthovenn2.bioinfotoolkits.net/home) (Wang et al., 2015). Whole-genome-based phylogenetic analysis was performed with RAxML within Pathosystems Resource Integration Center (PATRIC) database using the Pcc ICMP 5702 genome (Stamatakis, 2014).
The substrate sequence database of T2SS and T3SS were downloaded from BastionHub (https://bastionhub.erc.monash.edu/download.jsp) (Wang et al., 2021). BLASTp was performed in Linux environment using command line interface against the query (P. carotovorum ICMP 5702) to predict the potential type II and III effector protein sequences. The Uniprot IDs of the protein hits obtained through BLASTp were uploaded on UniProt database (https://www.uniprot.org/uploadlists/) for finding basic information about protein sequences and associated detailed annotation.
The amino acid sequences of P. carotovorum ICMP 5702 were downloaded in FASTA format from RAST and screened for carbohydrate-active modules using dbCAN Carbohydrate-active enzyme Annotation (http://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/blast.php) (Zhang et al., 2018). Sequences associated with glycosyl transferase activity and intracellular function were not included in analysis. Putative cell wall degrading enzymes associated with carbohydrate-binding modules and enzymes such as glycoside hydrolase (GH), polysaccharide lyase (PL), and carbohydrate esterase (CEs) were identified using default parameters.
The genome of Pcc ICMP 5702 is linear, composed of 46 contigs and is 4,774,457 bp in size. The average G + C content of the whole genome is 51.90%. The N50 value is 448,171 bp. In addition to 4,520 protein coding genes (CDSs), the chromosome contains 72 tRNAs and 12 rRNAs including nine 5S rRNAs, two 16S rRNAs, and one 23S rRNA. The genome contains 232 predicted tandem repeats (Table 1, Fig. 1). Most of these features were found identical to the previously annotated genome (Panda et al., 2015). However, three prophage regions were identified one of which was 41.1 kb in size having 54 proteins.
A total of 4,520 protein encoding genes (PEGs) and 83 RNAs were predicted in the genome of Pcc ICMP 5702 of which 1,331 genes was annotated to 344 subsystems (Fig. 2, Supplementary Table 1). Altogether, additional 411 coding sequences were obtained as compared to previous annotation (Panda et al., 2015). The annotated genome has highest number of genes associated with amino acids and derivatives (n = 312, 6.90%), protein metabolism (n = 199, 4.40%), Co-factors, prosthetic groups and pigments (n = 158, 3.49%), and membrane transport (n = 133, 2.94%). Additionally, a large set of genes associated with protein secretion including type I (15 genes), type II (23 genes), type III (21 genes), type IV (27 genes), type V (5 genes), and type VII (Chaperone/Usher pathway, CU) (5 genes) were also identified. RAST annotation revealed that strain Pectobacterium atrosepticum SCRI1043 and Serratia proteamaculans 568 are the closest neighbors of Pcc ICMP5702.
The gene ontology (GO) analysis grouped 3860 genes into the molecular function, cellular component and biological process categories (Fig. 3, Supplementary Table 2). Majority of the genes were predicted to encode molecular function, followed by cellular component and biological process. In the molecular function domain, the highest abundance of genes was represented by ‘DNA binding’ (n = 326, 7.21%), followed by ‘ATP binding’ (n = 264, 5.84%), ‘Hydrolase activity’ (n = 197, 4.35%), and ‘Metal ion binding’ (n = 155, 3.42%). In the cellular component category, the GO term ‘Integral component of membrane’ (n = 945, 20.9%) was the largest group, followed by ‘Plasma membrane’ (n = 567, 12.54%) and ‘Cytoplasm’ (n = 450, 9.95%). In the biological process domain, ‘Membrane transport’ (n = 319, 7.05%) represented the largest group of genes, followed by ‘Transcription’ (n = 228, 5.04%), ‘Proteolysis’ (n = 106, 2.34%) and ‘Phosphorylation’ (n = 71, 1.57%).
Search against the cluster of orthologous group (COG) database resulted in the assignment of COG classification for 4,520 genes into 19 orthologous categories (Fig. 4, Supplementary Table 3). The clusters for ‘Transcription’ (n = 355, 7.85%), ‘Inorganic ion transport and metabolism’ (n = 338, 7.47%), ‘Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis’ (n = 263, 5.81%), and ‘Energy production and conversion’ (n = 233, 5.15%) formed the largest group. The category for ‘Cell motility’, ‘Transport and catabolism’ and ‘Defence mechanisms’ represented the smallest groups with 51, 45, and 44 genes, respectively. Besides, the clusters for ‘Amino acid transport and metabolism’ (n = 224, 4.95%), ‘Carbohydrate transport and metabolism’ (n = 217, 4.80%), ‘Coenzyme transport and metabolism’ (n = 201, 4.44%), and ‘Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis’ (n = 195, 4.31%) were substantially represented.
Of the 3860 annotated genes with GO terms, 1,355 genes were assigned EC numbers and mapped into 54 KEGG categories (Fig. 5, Supplementary Table 4). Among the five main categories, largest number of genes were represented by ‘Metabolism’ (n = 1,835, 40.59%) and ‘Environmental information processing’ (n = 451, 9.97%). Six sub-pathways, namely ‘Carbohydrate metabolism’ (n = 369, 8.16%), ‘Amino acid metabolism’ (n = 315, 6.96%), ‘Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites’ (n = 312, 6.90%), ‘Membrane transport’ (n = 298, 6.59%), ‘Microbial metabolism in diverse environments’ (n = 187, 4.13%), and ‘Signal transduction’ (n = 153, 3.38%) were significantly enriched in the Pcc ICMP5702 genome. This suggest that Pcc ICMP5702 has a highly activated metabolic pathway for its growth, development and pathogenicity.
Assessment of the amino acid composition, dipeptide composition and similarity-search based PSI BLAST categorized 1,780 virulent proteins encoded by Pcc ICMP 5702. Further, the resistance gene finder tool of CARD found that seven PEGs of the Pcc ICMP 5702 chromosome have similarity with the antibiotic resistant proteins exhibiting resistance to multiple drug classes including Fluoroquinolone, Carbapenem Diaminopyrimidine, Phenicols and Cephalosporin. CRISPR-Cas Finder also showed that Pcc ICMP 5702 consisted eight CRISPR repeat regions. Among the CRISPR sequences, the longest CRISPR repeat was 760 bp with 12 spacers. The shortest CRISPR was 95 bp with one spacer.
The genome of Pcc ICMP 5702 was compared with Pcc PCC21 (CP003776.1), Pcc WPP 14 (CP051652), Pcc S1 (CP063773) as well as Pcb SX309 (CP020350), and Pco BCS7 (CP009678.1) to determine the genomic similarity at the species as well as subspecies level. Results showed that Pcc ICMP 5702 (4,774,457 bp) has a smaller genome than the counterparts. The ANI, and the in silico DDH showed that Pcc ICMP5702 and Pcc WPP14 were clustered closely and occupied the same taxonomic position. Alignment of the whole genome sequences from the six strains revealed that Pcc ICMP5702 is evolutionarily closer to Pcc 21 and Pcc WPP14 (Fig. 6A, Supplementary Table 5). At the subspecies level, Pcc ICMP5702 was found closer to Pco BCS7 than to Pcb SX309. There is no significant gene insertion or deletion of large regions in Pcc ICMP5702, but large local collinear blocks inversion were found in Pco BCS7 and Pcb SX309 and the locations of homologous genes were different (Fig. 6B).
The core genome of Pcc ICMP5702, Pcc S1, Pcc 21, and Pcc WPP14 is composed of 3448 orthologous genes. Pcc ICMP 5702 displayed 9 unique gene families while it shared 51 genes with Pcc S1, 46 genes with Pcc 21 and 203 genes with Pcc WPP14 genome (Fig. 6C). There were 3443 orthologous genes shared by the three subspecies of P. carotovorum (Fig. 6D). Pcc ICMP5702 shared 261 genes with Pcb SX309 and 237 genes with Pco BCS7 genome while 10 gene families were uniquely represented in Pcc ICMP 5702. The members of the unique gene families from Pcc ICMP5702 were associated with movement of cell or subcellular component (GO: 0006928), locomotion (GO: 0040011), localization (GO: 0051179), DNA modification (GO: 0006304), biological process (GO: 0008150), response to stimulus (GO: 0050896), and nucleic acid binding (GO: 0003676).
Effector proteins play an important role in infection and pathogen virulence because of their ability to inactivate host defences. The type II and type III secreted effector proteins from Pcc ICMP5702 were predicted through a BLASTp search of the BastionHub database containing sequences of substrates secreted by gram-negative bacteria (T1SE-T4SE and T6SE). A total of 28 and 63 PEGs of Pcc ICMP5702 showed at least some similarity to type II and type III secreted effector proteins, respectively (Tables 2 and 3). The BLASTp results revealed that Pcc ICMP5702 produce major type II effector proteins including endo-polygalacturonase (PehA), Prt (LasA), Pel, glycerophosphoryl diester phosphodiesterase, chitinase, alkaline phosphatase L, and haloprotease. Majority of the predicted T2SS effectors were associated with extracellular region (GO: 0005576) and periplasmic space (GO: 0042597) and involved in protein transport by the Sec complex (GO: 0043952) (Supplementary Table 2).
Likewise, major type III effector genes including the hrpN, hrpC, the Hop (AK1, AN1, and AL1) genes, dspE gene encoding AvrE-family T3SS effectors, H(+)-transporting two-sector ATPase, and harpin HrpW with Pel domain which contribute to effector protein translocation and disease were predominantly expressed in Pcc ICMP 5702. Majority of the predicted T3SS effectors were associated with outer extracellular region (GO: 0005576), cytoplasm (GO: 0005737), and cell membrane (GO: 0016021). The effectors were mostly involved in polysaccharide catabolic process (GO: 0000272), lyase activity (GO: 0016829), Peh activity (GO: 0004650), pectin lyase activity (GO: 0047490), and phosphoric diester hydrolase activity (GO: 0008081) (Supplementary Table 3).
To determine the pathogenicity factors, present in Pcc ICMP 5702, we mined the genome to detect the previously known pathogenic determinants including the PCWDE. Sequence search analysis using dbCAN revealed that 181 genes from Pcc ICMP 5702 encoded carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) (Table 2). A total of 30 putative PCWDEs were classified into five GH, one CE, and three PL families. Cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin, xylan, and rhamnogalactonurate are the substrates of the carbohydrate active enzymes found in Pcc ICMP5702. Major groups of pectinolytic enzymes having pectin methylesterase (CE 8), Pel (PL 1), Peh (GH 28), and exo-poly-alpha-galacturonosidase (GH 28) were predicted in Pcc ICMP 5702. Additionally, Cel such as β-1,4-glucanase (GH 5), hydrolase alpha-galactosidase (GH 53) and xylanases such as alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase II (GH 5) and xylan 1,4-beta-xylosidase (GH 1) which degrade the linear polysaccharide xylan into xylose by catalysing the hydrolysis of the glycosidic linkage (β-1,4) of xylosides were also identified. Further, Pcc ICMP 5702 genome have three genes encoding arabinogalactan endo-1,4-beta-galactanase (GH 3) protein that are primarily involved in the degradation of arabinogalactans found in the cell wall of dicot plants.
Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum is a ubiquitous pathogen with a broad host range. There has been reclassification in the taxonomic position of strains in the Pectobacterium genus in recent years (Li et al., 2018). For instance, P. peruviense, P. polaris, and Candidatus P. maceratum were separated from P. carotovorum and classified as three different species (Dees et al. 2017; Waleron et al. 2017). In the present study, the ANI, DDH values, and phylogenetic analysis indicated that Pcc ICMP 5702 and Pcc WPP14 were clustered closely and occupied the same taxonomic position. The annotated Pcc ICMP5702 genome contained highest number of genes associated with membrane transport, binding, transcription and carbohydrate metabolism. These annotations provide a basis for exploring the processes and pathways involved in the development and pathogenicity of Pcc ICMP5702.
Understanding the bacterial metabolism is important as it provides a shape to the host-pathogen interface. Bacterial pathogens have evolved to exploit hosts as a rich source of nutrients to support survival and replication through various metabolic pathways which aid to permit successful colonization in the host. Notably, recent research has stated that gluconate metabolism is required for virulence of the Pcc ICMP 5702. A mutant with a deletion-insertion within the operon controlling gluconate metabolism exhibits attenuated growth on its hosts, including potato and Arabidopsis thaliana and misregulation of virulence regulators KdgR and FlhD (Mole et al., 2010). Genes encoding flagella-based motility, siderophores, virulent proteins, phage proteins, and cell membrane structures such as LPS are present in Pcc ICMP 5702. Moreover, in this study, genome annotation also revealed that genes associated with microbial metabolism in diverse environments are substantially present in Pcc ICMP 5702. This is important in the aspect of microbial adaptation and the ability of phytopathogens including Pectobacterium to adapt and survive under unfavorable conditions in various ecological environments like sea water, fresh surface water, ground water, soil, etc. These adaptations result in the formation of resistance to various stress factors: oxidative stress, heat shock, and antibiotic treatment (Petrova et al., 2016). Genes for resistance to antibiotics and toxic compounds such as fluoroquinolones and beta lactamase have been identified in Pcc ICMP 5702. As a whole, Pectobacterium are suitable model microorganisms for studying microbial adaptation.
The key virulence factor of bacterial soft rot pathogen is PCWDEs. In this study, a total of 30 putative PCWDEs including Peh, Pel, Cel, and xylanases were identified in Pcc ICMP 5702. The regulation and functions of these Prt in pathogenicity of Pcc ICMP 5702 is yet to be determined. Bacteria have evolved several sophisticated secretion systems which act as cellular devices to export extracellular enzymes and effector proteins from the cytosol of the bacteria into the host cells. Thus, effectors directly play a role in the recognition process between the pathogen and the host. The functional description of effectors, microbial genomics and bioinformatics will help us to understand the host-pathogen interaction. T2SSs are conserved in most gram-negative bacteria, where they transport folded proteins from the periplasm into the extracellular environment. The T2SS operon contains 12-16 genes often arranged in a single operon, named general secretion pathway proteins: GspC to GspO (Nivaskumar and Francetic, 2014). The T2SS channel is only found in the outer membrane, proteins secreted through this apparatus must first be delivered to the periplasm. These proteins are first transported through the inner membrane by the general secretory (Sec) or twin-arginine translocation (Tat) pathways and then secreted from the periplasm into the extracellular medium by the T2SS effectors. Transport into periplasm requires an N-terminal signal sequence, and during transfer to the periplasm, the protein is processed by a signal peptidase. SignalP 4.0 server predicted a total of 585 proteins of ICMP5702 as putative signal peptides, out of which 412 proteins were classified as secretory signal peptides transported by the Sec translocon, 144 proteins as lipoprotein signal peptides and 29 proteins were Tat signal peptides. Previous studies have revealed that the T2SS machinery of the plant pathogens secretes a variety of CAZymes degrading plant cell wall such as pectinases, Cel, and lipases, Pel, and Peh, and its inactivation led to reduced pathogenicity (Filloux, 2004). The type II secreted effectors identified in Pcc ICMP 5702 included included Peh encoded by pehA, Pel by pelH and pelB, and alkaline phosphatase by phoA. A detail assessment of these factors will pave the way for unraveling the nature of pathogenicity in Pcc ICMP 5702.
The T3SS interferes with the host cell cytoskeleton to promote attachment and invasion, disrupts cellular trafficking processes, cytotoxicity and barrier dysfunction and subverts the host immune system. The genes encoding the T3SS are called the hrp (hypersensitive response and pathogenicity) and hrc (hypersensitive response and conserved) genes. Hrc proteins are highly conserved amongst plant and animal pathogens and are involved in the secretion of T3SS substrates across the bacterial envelope. In Erwinia amylovora, the T3SS is a major pathogenicity factor as the T3SS-deficient mutants are unable to cause fire blight disease in Rosaceous plant hosts (Oh and Beer, 2005). The dspE gene encoding AvrE-family T3SS effectors, Harpin Hrp W with Pel domain and genes encoding metalloprotease were predicted in Pcc ICMP5702.
The type VI secretion system (T6SS) is the recently identified secretion system in diverse gram-negative bacteria which possibly participates in bacterial pathogenicity and has an effect on the Hcp secretion, biofilm formation and motility (Gallique et al., 2017). In the Pectobacterium genus, researchers have not been able to reach to a general conclusion for the biological functions of the T6SS. The functions of flagellar and chemotactic genes in Pectobacterium pathogenicity, primarily in pathogen-host plant interactions, are yet to be explored. The Pectobacterium strains also harbor the CRISPR-Cas immune system genes, which are suggested to contribute to bacterial virulence and adaptive immunity. However, the functions of these genes are yet to be elucidated in Pcc. Compared to other pathogenic bacteria belonging to the Pectobacterium genus, the genome of Pcc ICMP5702 encodes many similar virulence factors, including the PCWDEs, T2SS, T3SS, and flagellin encoded proteins. Characterization of the putative effectors through extracellular enzyme assays and transient expression assays could define their potential role in virulence of Pcc ICMP 5702.
A comprehensive characterization of the genetic features of Pcc ICMP 5702 was performed in this study. Genome annotation revealed the presence of encoding pathogenicity or virulence-related factors such as PCWDE, flagella-based motility factors, cell membrane structures, and secretion systems. The study also identified putative signal peptides involved in secretory pathway and revealed the presence of CRISPR repeats and antibiotic resistance genes in the genome. The identification of these factors provides insights into the mechanisms used by Pcc to invade the host machinery. The identification of prominent type II secreted effectors and type III secreted effectors of Pcc ICMP 5702 provides insights into the specialized secretion systems used by gram-negative pathogens to inject effectors into the host cell. Comparative analysis revealed the orthologous clusters which could be significant to delineate the evolutionary history of Pcc ICMP 5702. Overall, this study provides a framework for the future studies of effector proteins that are critical to host-parasite interaction, molecular mechanisms of pathogenesis and relation between Pectobacterium and other phytopathogens.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Vice Chancellor, Rama Devi Women’s University for her guidance and support. Dr Joshi’s lab is supported by research grants from the Dept. of Biotechnology (BT/PR23412/BPA/118/284/2017), Govt of India and Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) (EMR/2016/005234), Dept. of Science & Technology (DST), Govt of India.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary materials are available at The Plant Pathology Journal website (http://www.ppjonline.org/).
Fig. 1
Sub-system distribution of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum ICMP 5702. One thousand three hundred thirty-one protein encoding genes were annotated into 344 subsystems.
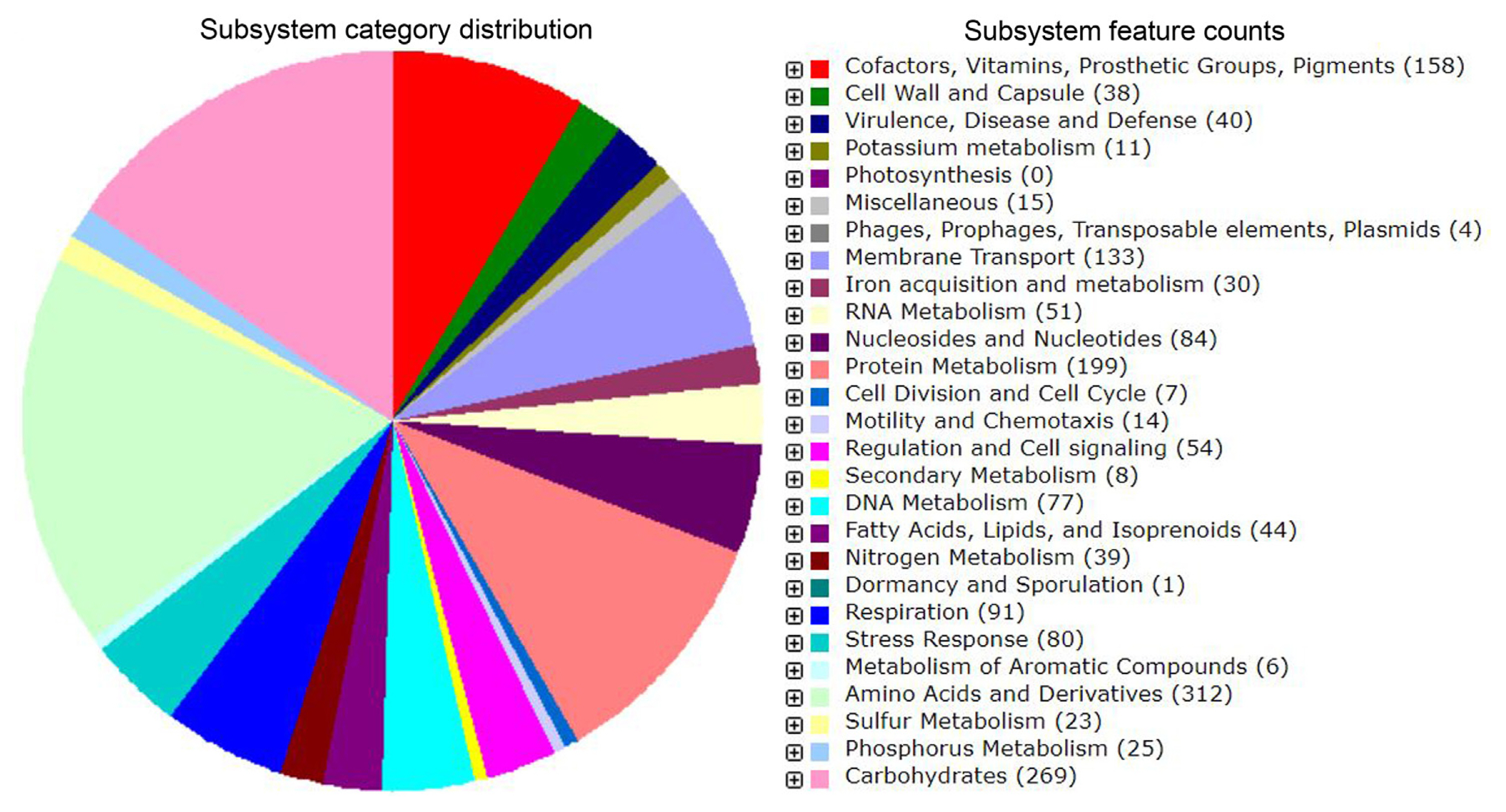
Fig. 2
Map of the Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum ICMP 5702 genome developed using CGview Server. From outside to centre, Rings 1 and 2 denote genes on forward and reverse strand respectively. Ring 3 shows GC skews, where green indicates positive values and purple indicates negative values. The innermost ring shows G + C% content plot (black). CDS, protein coding sequence; ORF, open reading frame.
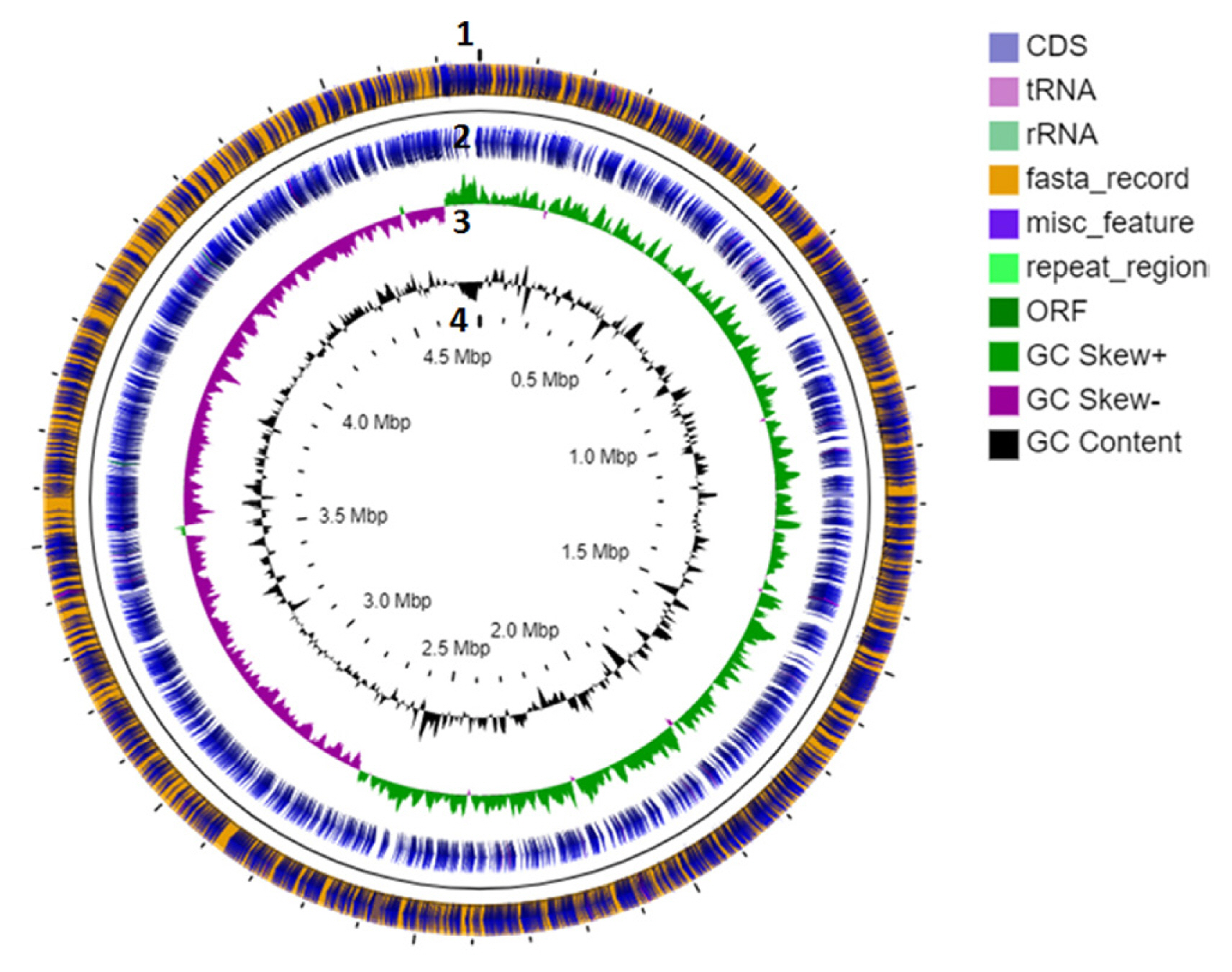
Fig. 3
Gene ontology (GO) classification of protein encoding genes from Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum ICMP 5702. GO terms were assigned to unigenes based on significant hits against the Nr database. Unigenes were assigned into three main categories: biological process (A), molecular function (B), and cellular component (C).
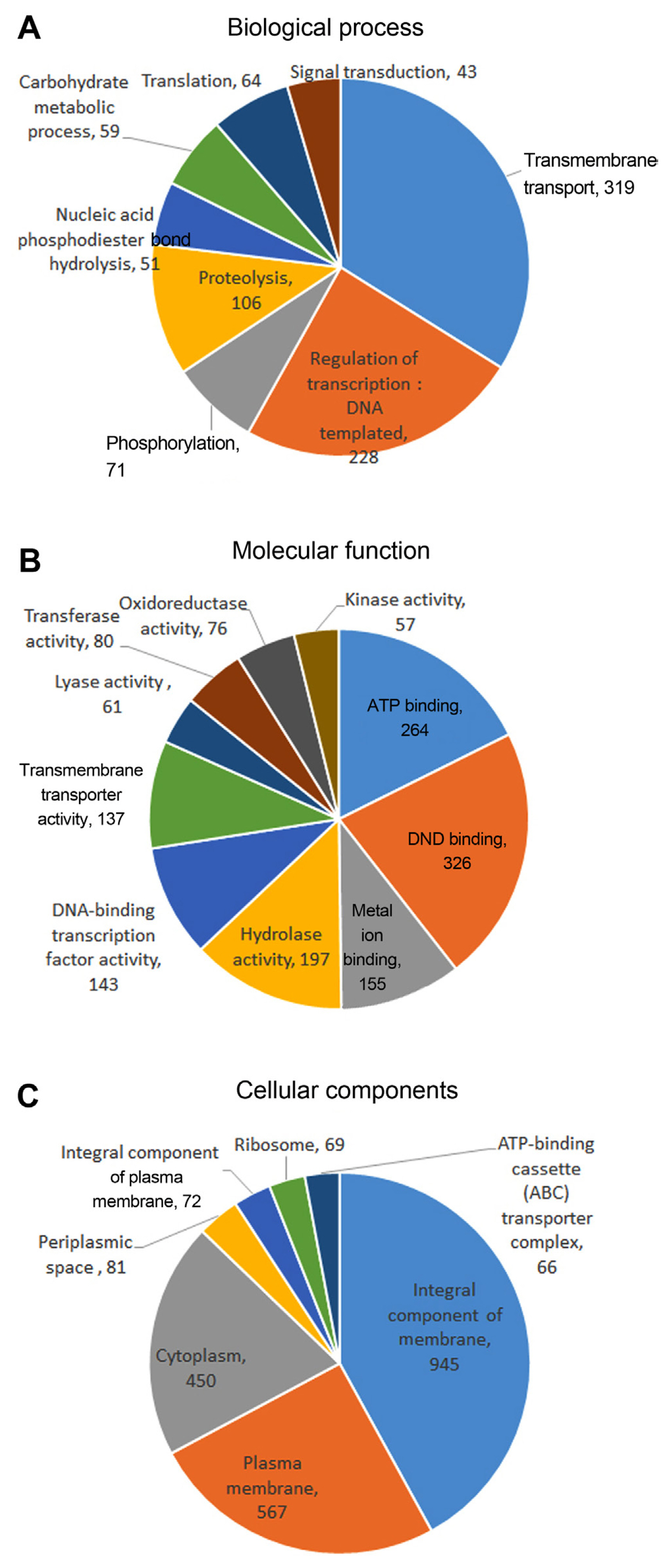
Fig. 4
Cluster of orthologous group (COG) functional annotation of protein encoding genes (PEGs) from Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum (Pcc) ICMP 5702. Four thousand five hundred twenty PEGs had a COG classification. PEGs from Pcc ICMP 5702 were grouped into 19 COG categories.
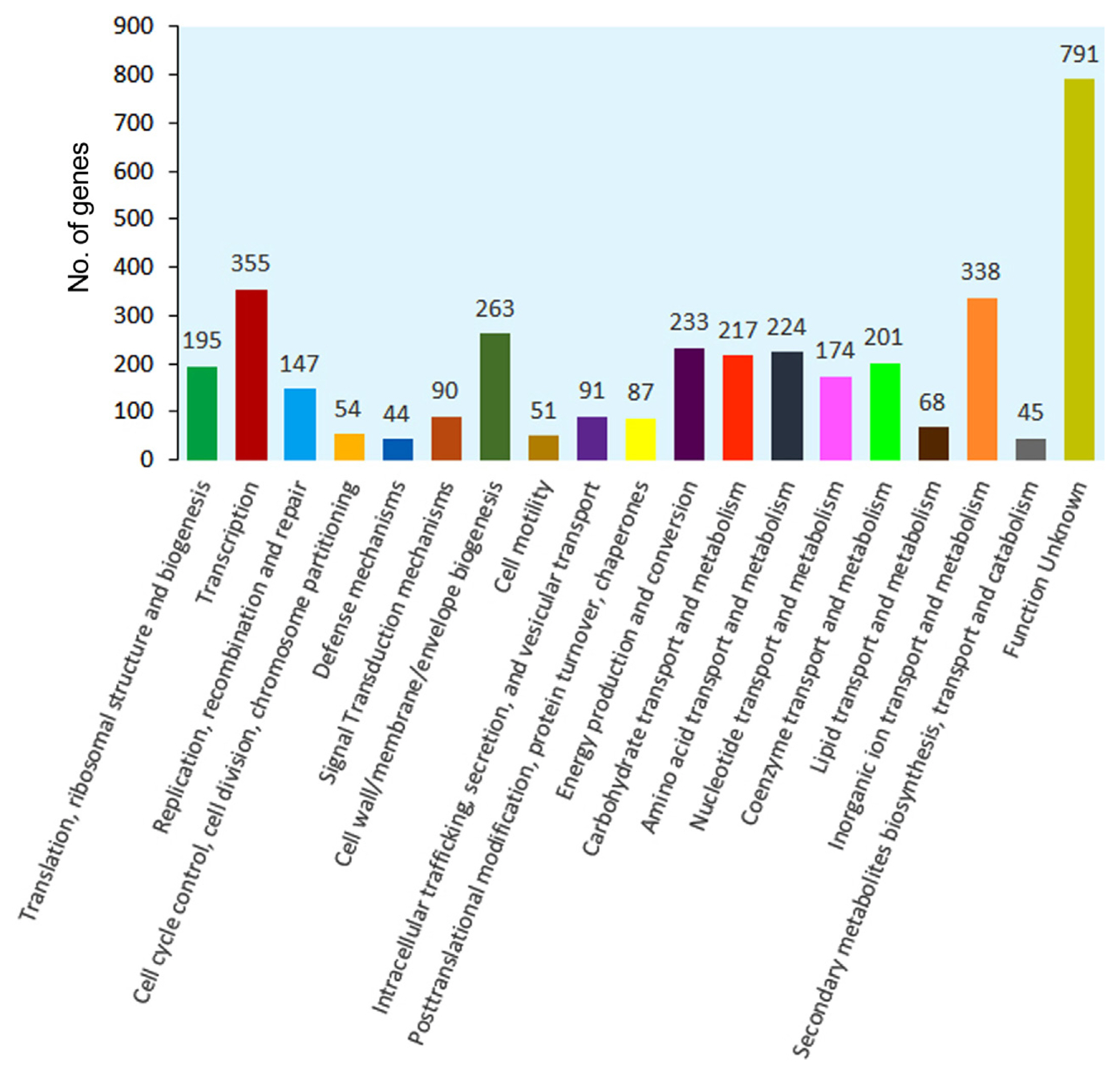
Fig. 5
Pathway assignment to Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum ICMP 5702 protein encoding genes (PEGs) based on Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway. PEGs were grouped into five major pathway categories as mentioned in the right panel.
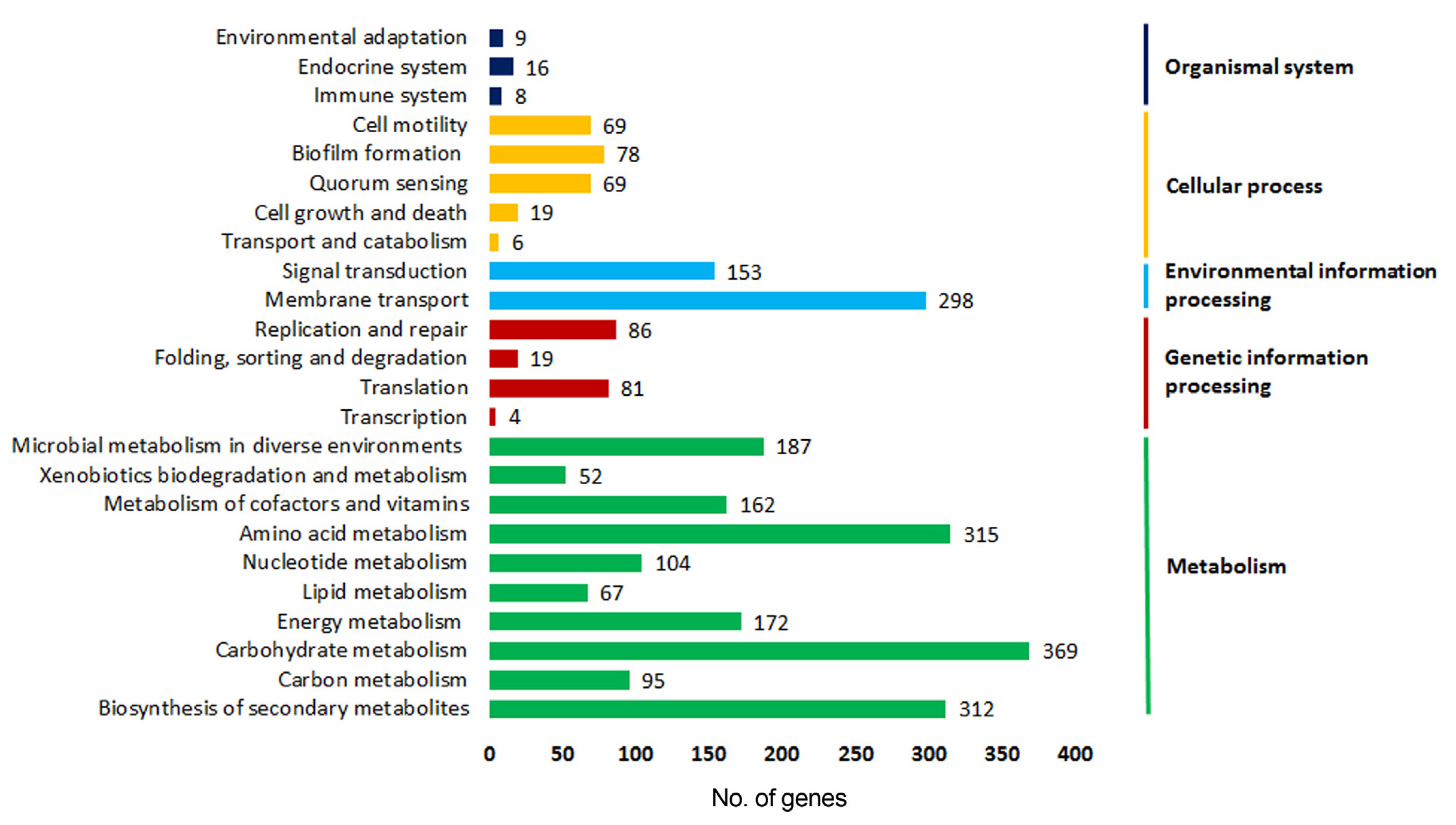
Fig. 6
Comparison of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum (Pcc) ICMP 5702 genome sequences with the genome of other Pectobacterium spp. (A) Mauve progressive alignment of Pcc ICMP 5702, PCCS1, WPP14, and PCC21 genomes. (B) At subspecies level, mauve progressive alignment of Pcc ICMP 5702 genome with SX309 and BCS7 genomes. (C, D) Venn diagram showing the number of clusters of orthologous genes shared and unique at species and subspecies level respectively.

Table 1
Genomic features of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum ICMP 5702
The data features were generated after re-annotation of the genome originally annotated by Panda et al. (2015).
Table 2
Protein encoding genes associated with type II secreted effectors in Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum ICMP 5702
Table 3
Protein encoding genes associated with type III secreted effectors in Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum ICMP 5702
References
Alcock, B. P., Raphenya, A. R., Lau, T., Tsang, K. K., Bouchard, M., Edalatmand, A., Huynh, W., Nguyen, A. V., Cheng, A. A., Liu, S., Min, S. Y., Miroshnichenko, A., Tran, H. K., Werfalli, R. E., Nasir, J. A., Oloni, M., Speicher, D. J., Florescu, A., Singh, B., Faltyn, M., Hernandez-Koutoucheva, A., Sharma, A. N., Bordeleau, E., Pawlowski, A. C., Zubyk, HL., Dooley, D., Griffiths, E., Maguire, F., Winsor, G. L., Beiko, R. G., Brinkman, F. S. L., Hsiao, W. W. L., Domselaar, G. V. and McArthur, A. G. 2020. CARD 2020: antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 48:D517-D525.


Almagro Armenteros, J. J., Tsirigos, K. D., Sønderby, C. K., Petersen, T. N., Winther, O., Brunak, S., von Heijne, G. and Nielsen, H. 2019. SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 37:420-423.


Arndt, D., Grant, J. R., Marcu, A., Sajed, T., Pon, A., Liang, Y. and Wishart, D. S. 2016. PHASTER: a better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:W16-W21.



Auch, A. F., Klenk, H.-P. and Göker, M. 2010. Standard operating procedure for calculating genome-to-genome distances based on high-scoring segment pairs. Stand Genomic Sci. 2:142-148.



Aziz, R. K., Bartels, D., Best, A. A., DeJongh, M., Disz, T., Edwards, R. A., Formsma, K., Gerdes, S., Glass, EM., Kubal, M., Meyer, F., Olsen, G. J., Olson, R., Osterman, A. L., Overbeek, R. A., McNeil, L. K., Paarmann, D., Paczian, T., Parrello, B., Pusch, G. D., Reich, C., Stevens, R., Vassieva, O., Vonstein, V., Wilke, A. and Zagnitko, O. 2008. The RAST Server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics 9:75.



Benson, G. 1999. Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 27:573-580.



Carattoli, A., Zankari, E., García-Fernández, A., Voldby Larsen, M., Lund, O., Villa, L., Møller Aarestrup, F. and Hasman, H. 2014. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58:3895-3903.



Charkowski, A. O. 2018. The changing face of bacterial soft-rot diseases. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 56:269-288.


Coburn, B., Sekirov, I. and Finlay, B. B. 2007. Type III secretion systems and disease. Clin Microbiol. Rev 20:535-549.



Couvin, D., Bernheim, A., Toffano-Nioche, C., Touchon, M., Michalik, J., Néron, B., Rocha, E. P. C., Vergnaud, G., Gautheret, D. and Pourcel, C. 2018. CRISPRCasFinder, an update of CRISRFinder, includes a portable version, enhanced performance and integrates search for Cas proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:W246-W251.



Crépin, A., Barbey, C., Beury-Cirou, A., Hélias, V., Taupin, L., Reverchon, S., Nasser, W., Faure, D., Dufour, A., Orange, N., Feuilloley, M., Heurlier, K., Burini, J.-F. and Latour, X. 2012. Quorum sensing signaling molecules produced by reference and emerging soft-rot bacteria (Dickeya and Pectobacterium spp.). PLoS ONE 7:e35176.



Darling, A. C. E., Mau, B., Blattner, F. R. and Perna, N. T. 2004. Mauve: multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res. 14:1394-1403.



Davidsson, P. R., Kariola, T., Niemi, O. and Palva, E. T. 2013. Pathogenicity of and plant immunity to soft rot pectobacteria. Front. Plant Sci. 4:191.



Dees, M. W., Lysøe, E., Rossmann, S., Perminow, J. and Brurberg, M. B. 2017. Pectobacterium polaris sp. nov., isolated from potato (Solanum tuberosum). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 67:5222-5229.


Filloux, A. 2004. The underlying mechanisms of type II protein secretion. Biochim Biophys Acta 1694:163-179.


Gallique, M., Decoin, V., Barbey, C., Rosay, T., Feuilloley, M. G. J., Orange, N. and Merieau, A. 2017. Contribution of the Pseudomonas fluorescens MFE01 type VI secretion system to biofilm formation. PLoS ONE 12:e0170770.



Garg, A. and Gupta, D. 2008. VirulentPred: a SVM based prediction method for virulent proteins in bacterial pathogens. BMC Bioinformatics 9:62.



Hogan, C. S., Mole, B. M., Grant, S. R., Willis, D. K. and Charkowski, A. O. 2013. The type III secreted effector DspE is required early in Solanum tuberosum leaf infection by Pectobacterium carotovorum to cause cell death, and requires Wx(3-6)D/E motifs. PLoS ONE 8:e65534.



Huerta-Cepas, J., Szklarczyk, D., Heller, D., Hernández-Plaza, A., Forslund, S. K., Cook, H., Mende, D. R., Letunic, I., Rattei, T., Jensen, L. J., von Mering, C. and Bork, P. 2019. eggNOG 5.0: a hierarchical, functionally and phylogenetically annotated orthology resource based on 5090 organisms and 2502 viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D309-D314.


Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Kawashima, S., Okuno, Y. and Hattori, M. 2004. The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:D277-D280.



Kim, H.-S., Ma, B., Perna, N. T. and Charkowski, A. O. 2009. Phylogeny and virulence of naturally occurring type III secretion system-deficient Pectobacterium strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75:4593-4549.

Kim, H.-S., Thammarat, P., Lommel, S. A., Hogan, C. S. and Charkowski, A. O. 2011. Pectobacterium carotovorum elicits plant cell death with DspE/F but the P. carotovorum DspE does not suppress callose or induce expression of plant genes early in plant-microbe interactions. Mol. Plant.-Microbe. Interact. 24:773-786.


Kõiv, V., Andresen, L., Broberg, M., Frolova, J., Somervuo, P., Auvinen, P., Pirhonen, M., Tenson, T. and Mäe, A. 2013. Lack of RsmA-mediated control results in constant hypervirulence, cell elongation, and hyperflagellation in Pectobacterium wasabiae. PLoS ONE 8:e54248.



Krogh, A., Larsson, B., von Heijne, G. and Sonnhammer, E. L. 2001. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 305:567-580.


Lee, D. H., Lim, J.-A., Lee, J., Roh, E., Jung, K., Choi, M., Oh, C., Ryu, S., Yun, J. and Heu, S. 2013. Characterization of genes required for the pathogenicity of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum Pcc21 in Chinese cabbage. Microbiology 159:1487-1496.



Li, L., Yuan, L., Shi, Y., Xie, X., Chai, A., Wang, Q. and Li, B. 2019. Comparative genomic analysis of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense SX309 provides novel insights into its genetic and phenotypic features. BMC Genomics 20:486.



Li, X., Ma, Y., Liang, S., Tian, Y., Yin, S., Xie, S. and Xie, H. 2018. Comparative genomics of 84 Pectobacterium genomes reveals the variations related to a pathogenic lifestyle. BMC Genomics 19:889.



Mashavha, M. L. 2013. Characterisation of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense isolates causing blackleg and soft rot diseases of potato in South Africa. MS thesis. University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa.
Mole, B., Habibi, S., Dangl, J. L. and Grant, S. R. 2010. Gluconate metabolism is required for virulence of the soft-rot pathogen Pectobacterium carotovorum. Mol. Plant.-Microbe. Interact. 23:1335-1344.


Nivaskumar, M. and Francetic, O. 2014. Type II secretion system: a magic beanstalk or a protein escalator. Biochim Biophys Acta 1843:1568-1577.


Nykyri, J., Niemi, O., Koskinen, P., Nokso-Koivisto, J., Pasanen, M., Broberg, M., Plyusnin, I., Törönen, P., Holm, L., Pirhonen, M. and Palva, E. T. 2012. Revised phylogeny and novel horizontally acquired virulence determinants of the model soft rot phytopathogen Pectobacterium wasabiae SCC3193. PLoS Pathog. 8:e1003013.



Oh, C.-S. and Beer, S. V. 2005. Molecular genetics of Erwinia amylovora involved in the development of fire blight. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 253:185-192.


Panda, P., Lu, A., Armstrong, K. F. and Pitman, A. R. 2015. Draft genome sequence for ICMP 5702, the type strain of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum that causes soft rot disease on potato. Genome Announc. 3:e00875-15.



Petrova, O., Gorshkov, V., Sergeeva, I., Daminova, A., Ageeva, M. and Gogolev, Y. 2016. Alternative scenarios of starvation-induced adaptation in Pectobacterium atrosepticum. Res Microbiol. 167:254-261.


Portier, P., Pédron, J., Taghouti, G., Fischer-Le Saux, M., Caullireau, E., Bertrand, C., Laurent, A., Chawki, K., Oulgazi, S., Moumni, M., Andrivon, D., Dutrieux, C., Faure, D., Hélias, V. and Barny, M.-A. 2019. Elevation of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. odoriferum to species level as Pectobacterium odoriferum sp. nov., proposal of Pectobacterium brasiliense sp. nov. and Pectobacterium actinidiae sp. nov., emended description of Pectobacterium carotovorum and description of Pectobacterium versatile sp. nov., isolated from streams and symptoms on diverse plants. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 69:3207-3216.


Rodriguez, R. L. M. and Konstantinidis, K. T. 2016. The enveomics collection: a toolbox for specialized analyses of microbial genomes and metagenomes. PeerJ Prepr 4:e1900v1.
Salzberg, S. L. 2019. Next-generation genome annotation: we still struggle to get it right. Genome Biol. 20:92.



Stamatakis, A. 2014. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30:1312-1313.



Törönen, P., Medlar, A. and Holm, L. 2018. PANNZER2: a rapid functional annotation web server. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:W84-W88.



Toth, I. K., Bell, K. S., Holeva, M. C. and Birch, P. R. J. 2003. Soft rot erwiniae: from genes to genomes. Mol. Plant Pathol. 4:17-30.


Vercoe, RB., Chang, J. T., Dy, R. L., Taylor, C., Gristwood, T., Clulow, J. S., Richter, C., Przybilski, R., Pitman, A. R. and Fineran, P. C. 2013. Cytotoxic chromosomal targeting by CRISPR/Cas systems can reshape bacterial genomes and expel or remodel pathogenicity islands. PLoS Genet. 9:e1003454.



Waleron, M., Misztak, A., Waleron, M., Franczuk, M., Wielgomas, B. and Waleron, K. 2018. Transfer of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum strains isolated from potatoes grown at high altitudes to Pectobacterium peruviense sp. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 41:85-93.


Wang, J., Li, J., Hou, Y., Dai, W., Xie, R., Marquez-Lago, T. T., Leier, A., Zhou, T., Torres, V., Hay, I., Stubenrauch, C., Zhang, Y., Song, J. and Lithgow, T. 2021. BastionHub: a universal platform for integrating and analyzing substrates secreted by Gram-negative bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 49:D651-D659.


Wang, Y., Coleman-Derr, D., Chen, G. and Gu, Y. Q. 2015. OrthoVenn: a web server for genome wide comparison and annotation of orthologous clusters across multiple species. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:W78-W84.



- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- ORCID iDs
-
Raj Kumar Joshi

https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0505-2881 - Related articles



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement
Supplement Print
Print



