 |
 |
| Plant Pathol J > Volume 35(6); 2019 > Article |
Abstract
To detect Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni, a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) detection method were developed. The LAMP assay was designed to test crude plant tissue without pre-extraction, or heating incubation, and without advanced analysis equipment. The LAMP primers were designed by targeting an ABC transporter ATP-binding protein, this primer set was tested using the genomic DNA of Xanthomonas and non-Xanthomonas strains, and a ladder product was generated from the genomic DNA of X. arboricola pv. pruni strain but not from 12 other Xanthomonas species strains and 6 strains of other genera. The LAMP conditions were checked with the healthy leaves of 31 peach varieties, and no reaction was detected using either the peach leaves or the peach DNA as a template. Furthermore, the high diagnostic accuracy of the LAMP method was confirmed with 13 X. arboricola pv. pruni strains isolated from various regions in Korea, with all samples exhibiting a positive reaction in LAMP assays. In particular, the LAMP method successfully detected the pathogen in diseased peach leaves and fruit in the field, and the LAMP conditions were proven to be a reliable diagnostic method for the specific detection and identification of X. arboricola pv. pruni in peach orchards.
Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni is the causal agent of bacterial shot hole on a wide range of Prunus species, including apricot, plum, and peach trees (Ritchie, 1995; Vauterin et al., 1995). This pathogen causes necrotic lesions on the leaves, sunken lesions on the fruit, and cankers on the twigs, leading to serious crop losses (Park et al., 2010). In years, the loss of fruit among seriously susceptible cultivars can reach 100% (Ritchie, 1999). X. arboricola pv. pruni can be harbored in the budwood, meaning that the buds used for plant proliferation can spread the pathogen to other regions that were previously free of the disease (Goodman and Hattingh, 1986; Zaccardelli et al., 1998). New peach species that exhibit resistance to the disease have been studied and cultivated, however, no variant has successfully shown a plant defense reaction against the pathogen (Hammerschlag, 2000). Instead, effective phytosanitary detection methods have been considered helpful for the control of X. arboricola pv. pruni infections. Currently employed methods for the identification of X. arboricola pv. pruni are conventional PCR (Pagani, 2005), duplex PCR (Pothier et al., 2011), loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) detection (Bühlmann et al., 2013), lateral flow immunoassays (López-Soriano et al., 2017), and real-time PCR amplification (Garita-Cambronero et al., 2017; Palacio-Bielsa et al., 2011). Although efficient control of X. arboricola pv. pruni requires a rapid, sensitive, and reliable diagnosis system, however, these methods are inconvenient for field identification.
LAMP was originally reported by Notomi et al. in 2000 and has since become widely used for diagnosis because of its potentially rapid, accurate, cost-effective, and convenient amplification method (Notomi et al., 2000). The amplification products are stem-loop DNA structures shaped like cauliflower with multiple loops that are formed from various inverted repeats of the target (Iwamoto et al., 2003). The resulting amplicons are visualized by adding SYBR Green I to the reaction tube.
In this article, we describe the analysis of a Xap1 strain isolated from peach leaves with bacterial shot hole symptoms, which was identified as X. arboricola pv. pruni. Based on the genomic sequence of X. arboricola pv. pruni, we designed a LAMP primer system and optimized the LAMP reaction conditions using Xap1 as a positive control. The proposed LAMP method was successfully used in the diagnosis of the pathogen in field samples, providing simple and convenient field identification.
Peach leaves with bacterial shot hole symptoms were collected, and tissue sections from the lesions on the diseased leaves were disinfected with 70% ethanol, cut, crushed using a mortar and pestle in sterile distilled water, and serially diluted. Each diluted sample (100 μl) was spread onto nutrient-yeast-glycerol (NYG) agar (Tan et al., 2014) and incubated at 28°C for three days. On the plates containing the 10−3 diluted samples, 20-30 colonies appeared. The yellowish and transparent colonies were purified and identified. One positive strain was designated as Xap1, it was subcultured on NYG agar at 28°C and maintained in a glycerol suspension (20%, w/v) at −70°C.
The isolate was identified using 16S ribosomal RNA (Lane, 1991; Snaidr et al., 1997) and a putative ABC transporter ATP-binding protein gene sequence (Pagani, 2005; Pothier et al., 2011). The primers for the 16S rRNA gene sequence were 9F (5′-GAGTTTGATCCTGGCGGCTCAG-3′) and 1512R (5′-ACGGCTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′), targeting all bacterial members. In recent years, several bacterial genomes have been sequenced, however, the genes sequences can be partial due to the whole genome shotgun sequencing method, which limiting the prediction of genes structural and functional properties. It is known that the putative ABC transporter ATP-binding protein gene sequence is a species-specific sequence for X. arboricola pv. pruni and has been widely used for its identification (Pagani, 2005; Pothier et al., 2011), furthermore, it was well studied and the gene sequences are available on National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) website, therefore, the putative ABC transporter ATP-binding protein gene sequence was chosen as a target sequence for the identification of X. arboricola pv. pruni. Primers targeting the putative ABC transporter ATP-binding protein gene sequence were used for later confirmation, the forward and reverse primers used were Y17CoF (5′-GACGTGGTGATCAGCGAGTCATTC-3′) and Y17CoR (5′-GACGTGGTGATGATGATCTGC-3′), respectively. The Y17CoF/Y17CoR PCR primers are known for their detection of X. arboricola pv. pruni (Pagani, 2005). The LAMP primers were designed using PrimerExplorer V4 (http://primerexplorer.jp/e/), four primers were used in this study (Fig. 1): outer primers F3 (5′-AGACGTCTAGGGCAAGCC-3′) and B3 (5′-TGCTAGAACTGACGCTGAGA-3′) and inner primers FIP (5′-ATGGGGGCCCAATCTCTAGCAATTTTGTCGGGCGACAACTTCAAC-3′) and BIP (5′-TCCACACCGATTTGCAGAAGGATTTTCGTGAGTCAATCGCAGTGT-3′). A TTTT linker was added to the inner primer to form a loop structure.
Genomic DNA was extracted using the hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) purification method, which has been described previously (Ausubel et al., 1992). To amplify the 16S rRNA gene sequence and the putative ABC transporter ATP-binding protein gene sequence, the PCR condition was conducted as following: initial denaturation at 95°C for 5 min followed by 35 cycles at 95°C for 30 s, 55°C or 60°C for 30 s, 72°C for 1.5 min, and a final extension step at 72°C for 7 min. The obtained sequences were compiled using Seq-Man software (DNASTAR, Madison, WI, USA). Pairwise 16S rRNA gene sequence similarities with closely related species were calculated using both the EzBioCloud server (Yoon et al., 2017) and the BLAST search program at the NCBI website (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi). For species-level analysis, the specific sequence of the putative ABC transporter ATP-binding protein was analyzed using the BLAST search program on the NCBI website.
The LAMP reaction was contained 2 μl of 10× Bst reaction buffer, 0.5 μl of 10 mM dNTP, 0.5 μl of 10 pM F3 and B3, 2 μl of 10 pM FIP and BIP, and 1 μl of X. arboricola pv. pruni genomic DNA for a final volume of 19 μl (supplemented with double distilled water). To enhance the sensitivity of the LAMP assays, pre-heating took place at 60°C for 5 min. Following pre-heating, 1 μl of Bst DNA polymerase (8 units/μl, large fragment; New England Biolabs, Beverly, MA, USA) was added. To optimize the reaction temperature, the LAMP reaction was performed under various thermal conditions (50°C, 53°C, 55°C, 58°C, 60°C, 63°C, and 65°C). The resulting LAMP amplicons were visualized by adding 1 μl of 5-times diluted original SYBR Green I (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) to the reaction tube. A positive reaction was green, whereas the color remained orange to the naked eye for a negative reaction. An efficient reaction produced a white precipitate when visualized using a UV illuminator. Three microliters of LAMP products were electrophoresed using 2% agarose gels, followed by staining with ethidium bromide. And two microliters of LAMP products were digested by a restriction enzyme (HaeIII), followed by electrophoresis analysis.
The proposed LAMP method was applied for the diagnosis of field samples. Thirty-two peach varieties were used for the validation testing, 4 peach varieties were tested using diseased leaves, and 31 peach varieties were tested using healthy leaves. Diseased fruit collected from several peach orchards was also tested. All of the field samples were tested in triplicate, with peach leaf samples (diameter 1 cm) or fruit samples (0.05 g) ground in 300 μl of plant extraction buffer (200 mM Tris [pH 8.0]; 250 mM NaCl; 25 mM EDTA [pH 8.0]; 0.5% sodium dodecyl sulfate). The supernatant was diluted 10 times and then 1 μl of the diluted sample was used for the LAMP reaction. Two microliters of LAMP products were digested with the HaeIII restriction enzyme, with incubation at 37°C for 4 h. Electrophoresis was conducted using 2% agarose gels after enzyme digestion, followed by staining with ethidium bromide.
Colonies of the Gram-negative isolate Xap1 were grown on NYG agar at 28°C for 2 days. The cells were yellowish, glistening, circular, convex, mucous, slimy, and smooth. Comparative 16S rRNA gene sequence (1,398 bp) analysis revealed that strain Xap1 was phylogenetically affiliated with the members of the genus Xanthomonas, based on information from the EzBioCloud database. The 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity of Xap1 was investigated on the NCBI website, and it was found that it had a high similarity (100%) with various X. arboricola pv. pruni strains, such as 17-330, 17-328, 17-326, 17-324, 17-195, and a few X. campestris strains (MSSRF_2C28, YNCCT1, and YNCCT6). Due to the large number of closely related X. arboricola pv. pruni strains, it was impossible to identify isolate Xap1 at the species level using the 16S rRNA sequence alone. It is known that the putative ABC transporter ATP-binding protein gene sequence is unique to X. arboricola pv. pruni species and has been widely used for its identification. Therefore, the putative ABC transporter ATP-binding protein gene sequence (898 bp) obtained from Xap1 was analyzed using the BLAST search program on the NCBI website. According to the alignment, strain Xap1 exhibited 100% similarities with X. arboricola pv. pruni XAP HU1 and XAP HU2 (accession number: KY039173 and MG049921), and 99.78% similarities with X. arboricola pv. pruni BJ15 and CFBP 5530 (accession number: MF362224 and HQ896469). Moreover, the 16S rRNA gene and ABC transporter ATP-binding protein gene sequences of strain Xap1 were compared with the 13 X. arboricola pv. pruni strains (14-199, 15-096, 15-101, 15-106, 16-143, 16-153, 16-156, 16-244, 17-178, 17-195, 17-210, 17-213, and 17-215) which provided by Rural Development Administration, the 16S rRNA gene and ABC transporter ATP-binding protein gene sequences of strain Xap1 had a high similarity (100%) with the sequences derived from the thirteen X. arboricola pv. pruni strains. Based on this sequence data analysis, the isolate Xap1 was identified as X. arboricola pv. pruni. The 16S rRNA gene sequences of strains Xap1, 14-199, 15-096, 15-101, 15-106, 16-143, 16-153, 16-156, 16-244, 17-178, 17-195, 17-210, 17-213, and 17-215 were deposited in NCBI GenBank with following accession number: LC507165, LC507166, LC507167, LC507168, LC507169, LC507170, LC507171, LC507172, LC507173, LC507174, LC507175, LC507176, LC507177, and LC507178, respectively.
To optimize the reaction conditions, the LAMP reaction was tested at various temperatures (Fig. 2). High efficiency was achieved at temperatures of 65°C, 63°C, 60°C, and 58°C for 45 min, with 60°C identified as the optimal temperature. The positive reactions all turned green after the addition of SYBR Green I, while the negative reactions remained orange. To confirm specific amplification, the LAMP products were digested with the HaeIII restriction enzyme, which produced predicted fragment sizes of 88 bp and 114 bp. The difference in the LAMP products before and after enzyme treatment was analyzed using electrophoresis (Fig. 3).
To determine the analytical sensitivity of LAMP testing, the genomic DNA purified from Xap1 was diluted down to the following concentrations: 1 (180 ng/μl), 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/10, 1/32, 1/50, 10−2, and 10−3 (Fig. 4). It was found that 1.8 ng/μl of genomic DNA could be detected by the LAMP reaction (Fig. 4, lane 8). To evaluate the species specificity of the designed primers, 12 other Xanthomonas species strains and six strains from other genera were tested using the LAMP reaction with their genomic DNA (Table 1), and specific PCR was used to compare the sensitivity of the proposed LAMP assays. All of the Xanthomonas and non-Xanthomonas strains were tested with PCR using primers Y17CoF/Y17CoR. It was found that the LAMP assay was more accurate than the traditional PCR method, with only the strain Xap1 producing a positive reaction in the LAMP test, while two strains of X. campestris pv. hyacinthi and Acidovorax facilis had positive reactions in the PCR test using primers Y17CoF/Y17CoR. LAMP specificity was also tested using 1 μl of genomic DNA from 31 healthy peach varieties (Table 2). It was subsequently found that the LAMP assay was able to specifically detect X. arboricola pv. pruni.
In addition, the LAMP method was tested with 13 X. arboricola pv. pruni strains isolated from various regions in Korea (Table 3). Conforming to the results for regular PCR analysis using the primers Y17CoF/Y17CoR, all of the X. arboricola pv. pruni strains exhibited a positive reaction in the LAMP assays, indicating that the proposed LAMP primer system can specifically diagnose the presence of X. arboricola pv. pruni.
The proposed LAMP assay was validated using plant samples from the field. For this purpose, healthy leaves and leaves with shot hole disease from naturally infected plants were tested. Leaf samples from 32 peach varieties were analyzed with the proposed LAMP assay (Table 2, Fig. 5A), and it was found that only the diseased leaves had a positive reaction, in particular, the LAMP assay were succeed for leaves without invisible symptoms, with the healthy leaves producing a negative reaction (Fig. 5B). Confirming the specific amplification, all of the positive LAMP products were digested by the HaeIII restriction enzyme (Fig. 5C). This indicates that the proposed LAMP assay successfully detected the pathogen X. arboricola pv. pruni in the diseased peach leaves. The effectiveness of the LAMP method was also validated on peach fruit bearing the bacterial shot hole disease (Fig. 5A), all of the diseased fruit had a positive reaction in the LAMP assays (Fig. 5B and C).
In conclusion, the LAMP method was successful in the rapid and accurate detection of field samples, confirming that it is a reliable diagnostic method for the specific detection and identification of X. arboricola pv. pruni in peach orchards in Korea.
X. arboricola pv. pruni is the cause of shot hole disease among Prunus spp. such as peaches, plums, and other stone fruits, which can lead to significant production losses. The pathogen can be epiphytic on its host or be harbored in propagative plant tissues, and can thus be easily spread. This study developed a LAMP assay to detect X. arboricola pv. pruni based on a species-specific DNA sequence. The sensitivity and specificity of the LAMP method were tested using various Xanthomonas and non-Xanthomonas strains. In comparison with traditional PCR, the LAMP method proved to be more accurate. Two strains of X. campestris pv. hyacinthi and Acidovorax facilis generated positive results in the PCR test using the primers Y17CoF/Y17CoR, while only the X. arboricola pv. pruni strain Xap1 produced a positive reaction using the LAMP assay (Table 1). The success of the proposed LAMP method was illustrated by the testing of 13 X. arboricola pv. pruni strains isolated from various regions in Korea (Table 3). Consequently, it can be concluded that this LAMP method can specifically diagnose the presence of X. arboricola pv. pruni.
The LAMP assay were able to test crude plant tissue without pre-extraction, or heating incubation, and it does not need advanced analysis equipment. It was successfully applied in field samples, the results were obtained by 45 min, with visual inspection, which supporting a high effective and easy processing method for plant quarantine.
In particular, the proposed LAMP assay achieved a high sensitivity and specificity 1.8 ng/μl of genomic DNA could be detected by the LAMP reaction (Fig. 4, lane 8), which was significantly higher than the traditional PCR method developed for identifying X. arboricola pv. pruni (Pagani, 2005). Leaves and fruits bearing the shot hole disease can be validate by the LAMP assay, particularly, the pathogen were successfully detected by using leaves without visible symptoms, which supporting the high sensitivity and accuracy of the proposed LAMP assay.
Relative methods for the identification of X. arboricola pv. pruni were reported, these authors conducted a range of tests on plant tissues, such as almond, apricot, and plum, which involved with LAMP method (Bühlmann et al., 2013), Bio-PCR method (Ballard et al., 2011), real-time PCR (Palacio-Bielsa et al., 2011), evaluation of a real-time PCR and the LAMP method (Palacio-Bielsa et al., 2015), and so on. Although their detection method is well developed, their method did not apply in Korea strains. It was reported that X. arboricola pv. pruni shows some genetic diversity in different geographic regions, such as Italy, Spain and Australia collections (Barionovi and Scortichini, 2008), Korean and West Europe collections (Park et al., 2009), even low genetic diversity were observed in Japan strains (Kawaguchi, 2014). Here, we developed a new LAMP method to test crude plant tissue without DNA preextraction, and it was successfully detected the pathogen in diseased peach leaves and fruit in Korea. The LAMP method was test with many X. arboricola pv. pruni strains which isolated from various geographic regions in Korea (Table 3), and it was validated by 32 peach varieties (Table 2), the results revealed that the target sequence is specific to X. arboricola pv. pruni and it do not have homology with peach genome. In comparison, the LAMP method developed in this study was simple and convenient, it was effectively detected the specific presence of X. arboricola pv. pruni in peach orchards in Korea, this effective detection method may help in improving control strategies for shot hole disease in the future.
Fig. 1
Schematic representation of the primer design for the proposed loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay showing the position of the six primers spanning the target gene and the nucleotide sequences of the putative ABC transporter ATP-binding protein gene sequence used to design the primers. The right arrow indicates a sense sequence used for the primer, while the left arrow indicates the complementary sequence used for the primer. The red arrowhead indicates a restricted enzyme site.
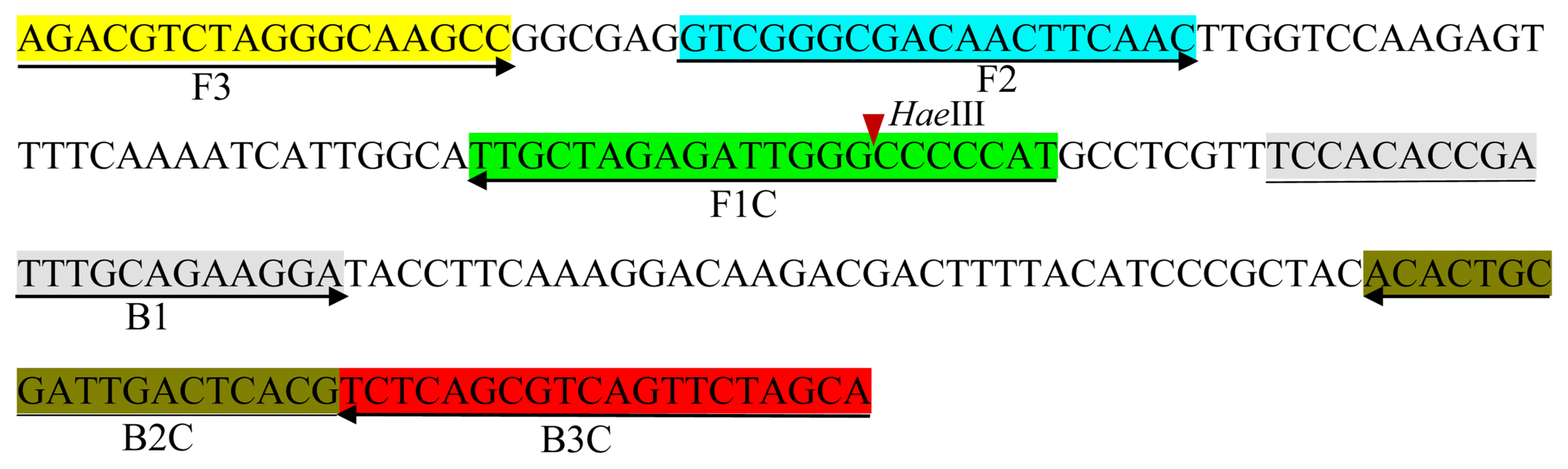
Fig. 2
Temperature optimization of the loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) primer set for the detection of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni. M: 1 kb plus DNA ladder; Lanes 1-7 indicate the LAMP reaction temperatures 65°C, 63°C, 60°C, 58°C, 55°C, 53°C, and 50°C, respectively.
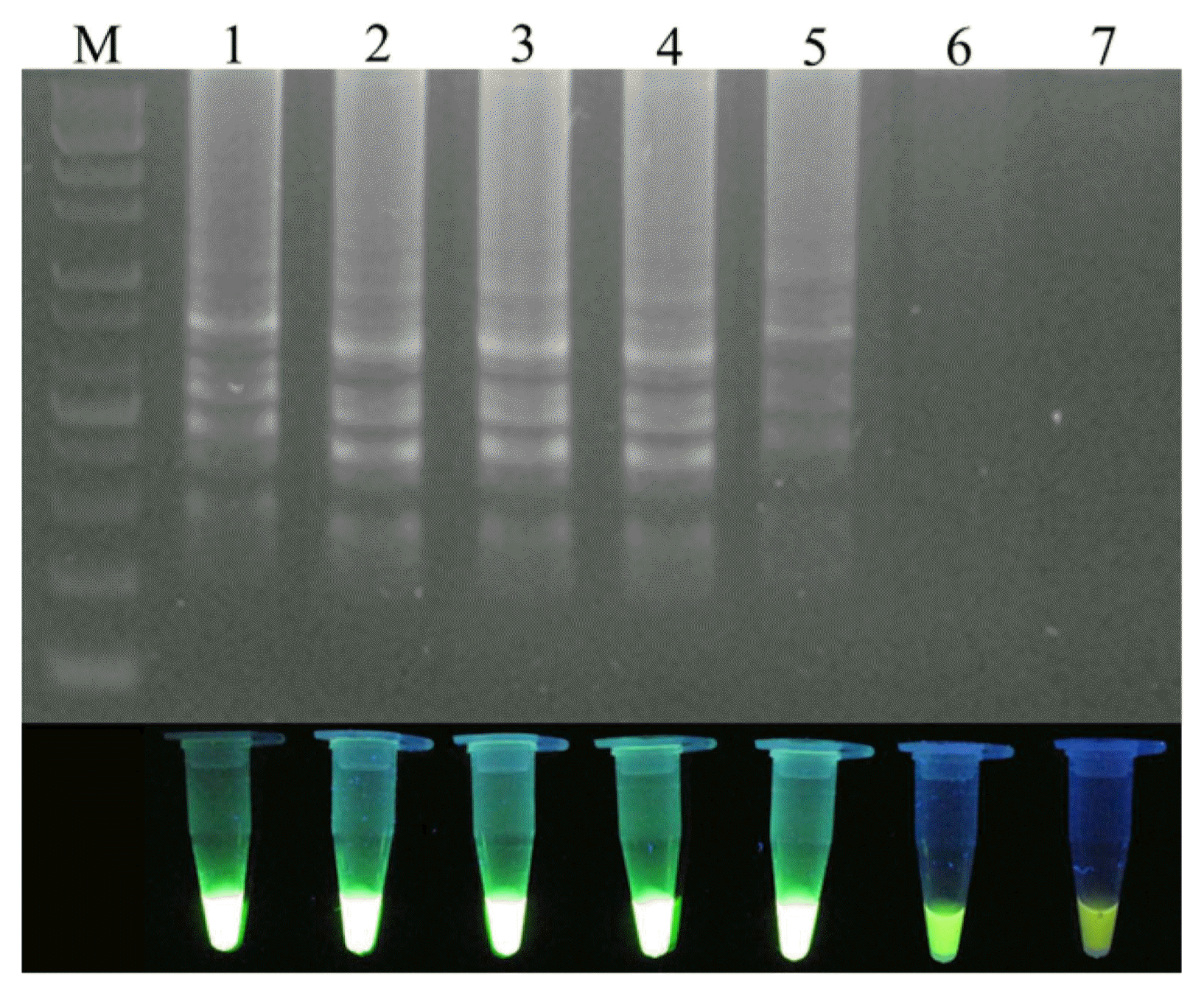
Fig. 3
Electrophoresis of the loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) products and the LAMP products digested with the HaeIII restriction enzyme. (A) Gel-imaging analysis of the LAMP product. M: 1 kb plus DNA ladder; Lanes 1-3 indicate positive control, negative control, and LAMP products digested with HaeIII, respectively. (B, C) Visual analysis after the addition of SYBR Green I using the naked eye and a UV illuminator, respectively.
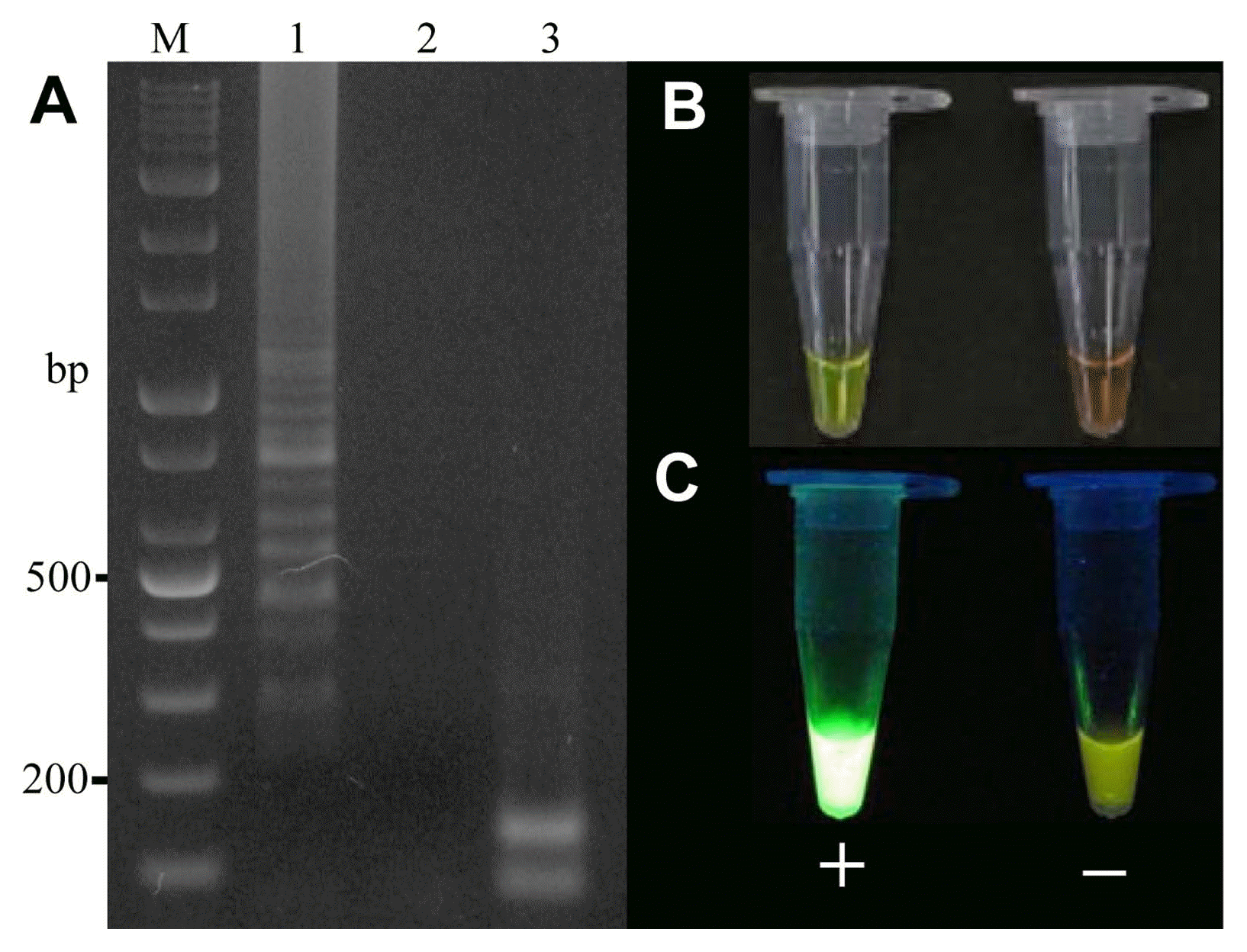
Fig. 4
Electrophoresis analysis of the loop-mediated isothermal amplification sensitivity test and visual analysis using a UV illuminator. M: 1 kb plus DNA ladder; lane 1: no dilution (180 ng/μl); lane 2: 1/2 dilution (90 ng/μl); lane 3: 1/4 dilution (45 ng/μl); lane 4: 1/8 dilution (22.5 ng/μl); lane 5: 1/10 dilution (18 ng/μl); lane 6: 1/32 dilution (5.6 ng/μl); lane 7: 1/50 dilution (3.6 ng/μl); lane 8: 10−2 dilution (1.8 ng/μl); lane 9: 10−3 dilution (0.18 ng/μl); lane 10: 10−4 dilution (0.018 ng/μl).
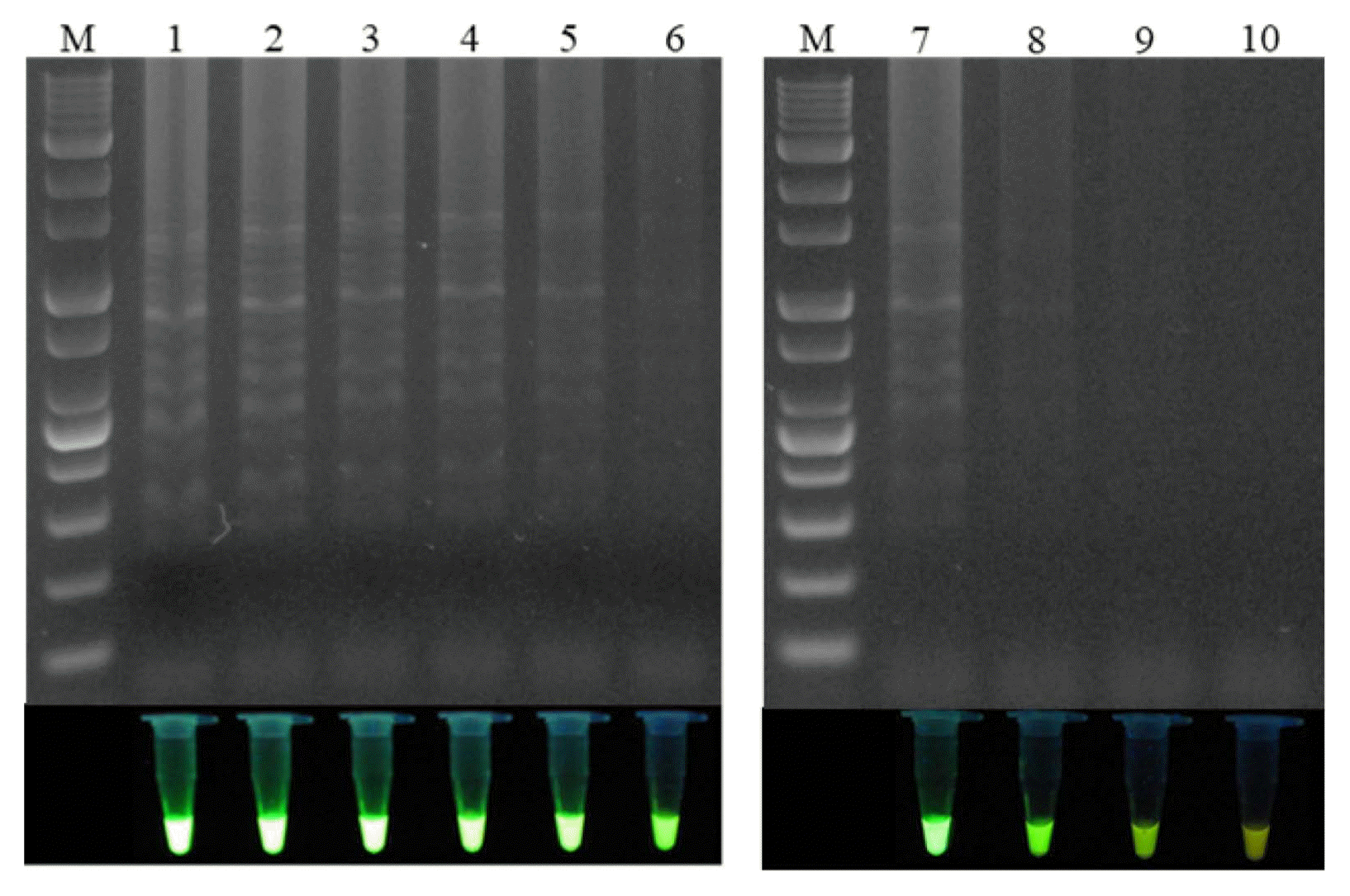
Fig. 5
Validation of the loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay using field samples. (A) Peach leaves and fruit samples collected from a peach orchard. Red arrows indicate the diseased areas. No. 1-10 indicate the following varieties of peach: Kanoiwa Hakuto, Changbangjosaeng, Baekmijosaeng, Cheonhong, DaehwaJosaeng, Daemyeong, Baekmijosaeng, Hakuho, Sulwooro 4-55, and Hikawa Hakuho, respectively; No. 11-13: peach fruit. (B) Electrophoresis analysis and visual analysis using a UV illuminator. M: 1 kb plus DNA ladder; P: positive control; N: negative control; Lanes 1-13 represent the LAMP results for samples No. 1-13, respectively. (C) Electrophoresis analysis of the LAMP products digested by HaeIII. P: positive control; Lanes 1-7 indicate the LAMP products digested by HaeIII from Daemyeong, Baekmijosaeng, Sulwooro 4-55, Hikawa Hakuho, and peach fruit 11-13, respectively.
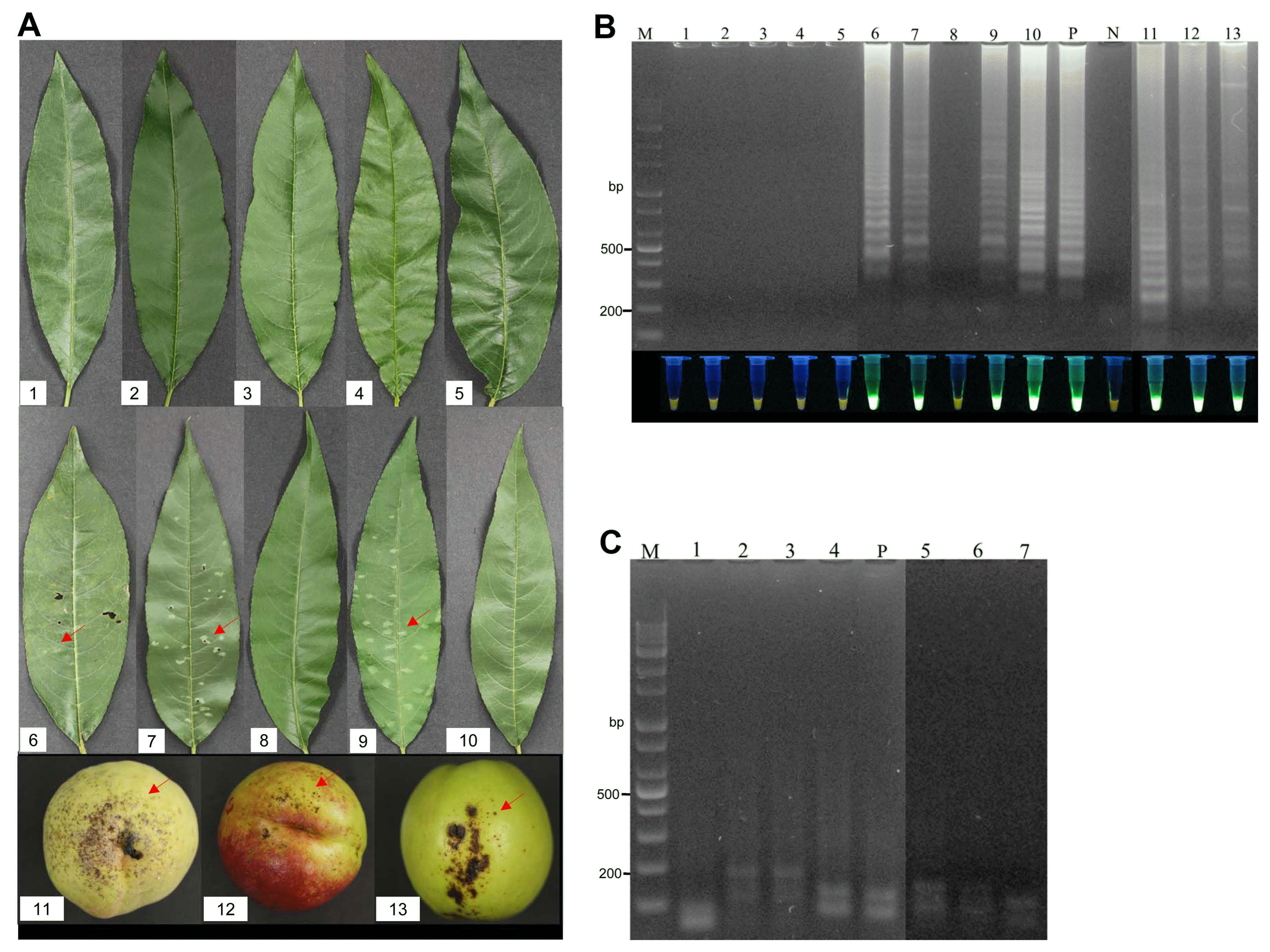
Table 1
Xanthomonas spp. and other bacterial strains used for the analysis of the specificity of the LAMP assays developed in this study
| Species | Strain | Host | PCRa | LAMPb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni | Xap1 | Peach | +c | + |
| X. axonopodis pv. phaseoli | KACC 10559 | Bean | − | − |
| X. axonopodis pv. citri | KCTC 2856 | Citrus | − | − |
| X. axonopodis pv. allii | LMG 25672 | Onion | − | − |
| X. campestris pv. malvacearum | KACC 12874 | Cotton | − | − |
| X. campestris pv. glycines | KACC 10491 | Soybean | − | − |
| X. campestris pv. zantedeschiae | NCPPB 4326 | White flowered calla lily | − | − |
| X. axonopodis pv. poinsettiicola | NCPPB 581 | Poinsettia | − | − |
| X. campestris pv. hyacinthi | NCPPB 205 | Hyacinth | + | − |
| X. campestris pv. campestris | LMG 559 | Crucifers | − | − |
| X. cucurbitae | LMG 8662 | Watermelon | − | − |
| X. oryzae pv. oryzae | KACC 10331 | Rice | − | − |
| X. translucens | KCTC 2751 | Cereal crops | − | − |
| Acidovorax facilis | LMG 2193 | NR | + | − |
| Burkholderia gladioli pv. alliicola | NCPPB 947 | Onion | − | − |
| B. caryophylli | NCPPB 2151 | Carnation | − | − |
| Spirosoma lituiforme | KCTC 52724 | NR | − | − |
| S. horti | KCTC 52728 | NR | − | − |
| S. humi | KCTC 52729 | NR | − | − |
Table 2
Peach varieties used for the validation of the LAMP assays developed in this study
| Health condition | Peach varieties | LAMP result | Peach varieties | LAMP result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diseased leaves (symptoms or no symptoms) | Daemyeong | +a | Sulwooro 4-55 | + |
| Baekmijosaeng | + | Hikawa Hakuho | + | |
|
|
||||
| Healthy leaves | Madoka | − | Keunhong | − |
| Hakuho | − | Subong | − | |
| Baekhyang | − | Baekmijosaeng | − | |
| Kanoiwa Hakuto | − | AmKing | − | |
| Changbangjosaeng | − | Prita | − | |
| Sin Hakuto | − | Sinbi | − | |
| Cheonhong | − | Sajajosaeng | − | |
| DaehwaJosaeng | − | Chiyomaru | − | |
| Kawanakajima Hakuto | − | Wolbongjosaeng | − | |
| Daemyeong | − | Miskayo | − | |
| Chiyomaru | − | Sunfre | − | |
| Hikawa Hakuho | − | Yume Fuji | − | |
| Yonghwang Baekdo | − | Hikawa Hakuho | − | |
| Akatsuki | − | Great Jumbo Akatsuki | − | |
| Red Start | − | Geumgang Sumil | − | |
| Takinosawa Gold | − | |||
Table 3
Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni strains isolated from various regions in Korea used for the LAMP specificity tests
| No. | Strain | Region | Peach varieties | Provided by | PCRa | LAMP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 14-199 | Gyeongbuk, Gimcheon | Fantazia | RDA | +b | + |
| 2 | 15-096 | Gyeonggi, Icheon | Changhowon Hwangdo | RDA | + | + |
| 3 | 15-101 | Chungbuk, Eumseong | Kawanakajima Hakuto | RDA | + | + |
| 4 | 15-106 | Jeonbuk, Jeongeup | Madoka | RDA | + | + |
| 5 | 16-143 | Jeonbuk, Buan | Changhowon Hwangdo | RDA | + | + |
| 6 | 16-153 | Chungbuk, Chungju | Kawanakajima Hakuto | RDA | + | + |
| 7 | 16-156 | Jeonbuk, Muju | Yumyeong | RDA | + | + |
| 8 | 16-244 | Chungnam, Cheongyang | Sungold | RDA | + | + |
| 9 | 17-178 | Jeonbuk, Jeonju | Mihong | RDA | + | + |
| 10 | 17-195 | Jeonbuk, Imsil | Madoka | RDA | + | + |
| 11 | 17-210 | Gyeongbuk, Yeongcheon | Fantazia | RDA | + | + |
| 12 | 17-213 | Chungnam, Yeongi | Madoka | RDA | + | + |
| 13 | 17-215 | Gyeongbuk, Gyeongsan | Cheonghong | RDA | + | + |
References
Ausubel, F.M., Brent, R., Kingston, R.E., Moore, D.D., Seidman, J.G., Smith, J.A. and Struhl, K. 1992. Current protocols in molecular biology. Vol.I: Greene Publishing Associates and Wiley Interscience, New York, NY.
Ballard, E.L., Dietzgen, R.G., Sly, L.I., Gouk, C., Horlock, C. and Fegan, M. 2011. Development of a Bio-PCR protocol for the detection of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni. Plant Dis. 95:1109-1115.


Barionovi, D. and Scortichini, M. 2008. Integron variability in Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis and Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni strains. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 288:19-24.


Bühlmann, A., Pothier, J.F., Tomlinson, J.A., Frey, J.E., Boonham, N., Smits, T.H.M. and Duffy, B. 2013. Genomics-informed design of loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detection of phytopathogenic Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni at the intraspecific level. Plant Pathol. 62:475-484.

Garita-Cambronero, J., Palacio-Bielsa, A., López, M.M. and Cubero, J. 2017. Pan-genomic analysis permits differentiation of virulent and non-virulent strains of Xanthomonas arboricola that cohabit Prunus spp. and elucidate bacterial virulence factors. Front Microbiol. 8:573



Goodman, C.A. and Hattingh, M.J. 1986. Transmission of Xanthomonas campestris pv. pruni in plum and apricot nursery trees by budding. HortScience. 21:995-996.

Hammerschlag, F.A. 2000. Resistant responses of peach somaclone 122-1 to Xanthomonas campestris pv. pruni and to Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae. HortScience. 35:141-143.

Iwamoto, T., Sonobe, T. and Hayashi, K. 2003. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for direct detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex, M. avium, and M. intracellulare in sputum samples. J Clin Microbiol. 41:2616-2622.



Kawaguchi, A. 2014. Genetic diversity of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni strains in Japan revealed by DNA fingerprinting. J Gen Plant Pathol. 80:366-369.

Lane, D.J. 1991. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics, eds. by E. Stackebrandt and M. Goodfellow, 115-175. Wiley, New York, USA.
López-Soriano, P., Noguera, P., Gorris, M.T., Puchades, R., Maquieira, Á., Marco-Noales, E. and López, M.M. 2017. Lateral flow immunoassay for on-site detection of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni in symptomatic field samples. PLoS ONE. 12:e0176201



Notomi, T., Okayama, H., Masubuchi, H., Yonekawa, T., Watanabe, K., Amino, N. and Hase, T. 2000. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:E63



Pagani, M.C. 2005. An ABC transporter protein and molecular diagnosis of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni causing bacterial spot of stone fruits. PhD thesis. North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA.
Palacio-Bielsa, A., Cubero, J., Cambra, M.A., Collados, R., Berruete, I.M. and López, M.M. 2011. Development of an efficient real-time quantitative PCR protocol for detection of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni in Prunus species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 77:89-97.


Palacio-Bielsa, A., López-Soriano, P., Bühlmann, A., van Doorn, J., Pham, K., Cambra, M.A., Berruete, I.M., Pothier, J.F., Duffy, B., Olmos, A. and López, M.M. 2015. Evaluation of a real-time PCR and a loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detection of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni in plant tissue samples. J Microbiol Methods. 112:36-39.


Park, S.Y., Lee, Y.S., Koh, Y.J., Hur, J.-S. and Jung, J.S. 2010. Detection of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni by PCR using primers based on DNA sequences related to the hrp genes. J Microbiol. 48:554-558.


Park, S.Y., Lee, Y.S., Shin, J.S., Koh, Y.J. and Jung, J.S. 2009. Genetic diversity of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni isolated in Korea. J Life Sci. 19:684-687.

Pothier, J.F., Pagani, M.C., Pelludat, C., Ritchie, D.F. and Duffy, B. 2011. A duplex-PCR method for species-and pathovar-level identification and detection of the quarantine plant pathogen Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni. J Microbiol Methods. 86:16-24.


Ritchie, D.F. 1995. Bacterial spot. In: Compendium of stone fruit diseases, eds. by J.M. Ogawa, E.I. Zehr, G.W. Bird, D.F. Ritchie, K. Uriu and J.K. Uyemoto, 50-52. APS Press, St. Paul, MN, USA.
Ritchie, D.F. 1999. Sprays for control of bacterial spot of peach cultivars having different levels of disease susceptibility, 1998. Fungic Nematic Tests. 54:63-64.
Snaidr, J., Amann, R., Huber, I., Ludwig, W. and Schleifer, K.H. 1997. Phylogenetic analysis and in situ identification of bacteria in activated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 63:2884-2896.



Tan, L., Rong, W., Lou, H., Chen, Y. and He, C. 2014. The Xanthomonas campestris effector protein XopDXcc8004 triggers plant disease tolerance by targeting DELLA proteins. New Phytol. 204:595-608.


Vauterin, L., Hoste, B., Kersters, K. and Swings, J. 1995. Reclassification of Xanthomonas. Int J Syst Evol Bacteriol. 45:472-489.

Yoon, S.H., Ha, S.M., Kwon, S., Lim, J., Kim, Y., Seo, H. and Chun, J. 2017. Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA and whole genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 67:1613-1617.



Zaccardelli, M., Malaguti, S. and Bazzi, C. 1998. Biological and epidemiological aspects of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni on peach in Italy. J Plant Pathol. 80:125-132.



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print




