 |
 |
| Plant Pathol J > Volume 37(6); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
Ralstonia syzygii subsp. indonesiensis (Rsi, former name: Ralstonia solanacearum phylotype IV) PW1001, a causal agent of potato wilt disease, induces hypersensitive response (HR) on its non-host eggplant (Solanum melongena cv. Senryo-nigou). The disaccharide trehalose is involved in abiotic and biotic stress tolerance in many organisms. We found that trehalose is required for eliciting HR on eggplant by plant pathogen Rsi PW1001. In R. solanacearum, it is known that the OtsA/ OtsB pathway is the dominant trehalose synthesis pathway, and otsA and otsB encode trehalose-6-phosphate (T6P) synthase and T6P phosphatase, respectively. We generated otsA and otsB mutant strains and found that these mutant strains reduced the bacterial trehalose concentration and HR induction on eggplant leaves compared to wild-type. Trehalose functions intracellularly in Rsi PW1001 because addition of exogenous trehalose did not affect the HR level and ion leakage. Requirement of trehalose in HR induction is not common in R. solanacearum species complex because mutation of otsA in Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum (former name: Ralstonia solanacearum phylotype I) RS1002 did not affect HR on the leaves of its non-host tobacco and wild eggplant Solanum torvum. Further, we also found that each otsA and otsB mutant had reduced ability to grow in a medium containing NaCl and sucrose, indicating that trehalose also has an important role in osmotic stress tolerance.
Ralstonia solanacearum species complex (RSSC) is well known as one of the most destructive bacterial plant pathogens due to its aggressiveness, extensive host range, broad geographical distribution, and long persistence under diverse environmental conditions (Genin, 2010; Meng, 2013; Prior et al., 2016). RSSC causes bacterial wilt disease in over 200 plant species worldwide and affects a wide range of economically important crops including tomato, potato, eggplant, chili, tobacco, banana, groundnut, and ginger (Du et al., 2017; Meng, 2013). R. solanacearum was ranked 2nd in a list of the top 10 most scientifically and economically important plant-pathogenic bacteria (Mansfield et al., 2012). RSSC has been classified into four phylotypes, depending on its geographical distribution and host plants. In 2014, Safni et al. proposed a new classification of RSSC and further taxonomic revision of the diverse group of strains in phylotype IV. Phylotype I and III are newly classified as R. pseudosolanacearum, phylotype II as R. solanacearum, and phylotype IV as R. syzygii. Then, R. syzygii was divided into three subspecies: R. syzygii subsp. syzygii, R. syzygii subsp. celebesensis, and R. syzygii subsp. indonesiensis (Rsi).
RSSC enters host plants through natural openings or wounds in the root system or at sites of secondary root formation, colonizes the cortex and vascular parenchyma, then enters the xylem vessels and rapidly spreads up into the stems and leaves (Du et al., 2017; Meng, 2013). This bacterium forms biofilms in the xylem, produces large amounts of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), and proliferates rapidly (Minh Tran et al., 2016; Mori et al., 2016). The rapid proliferation of bacteria and abundant EPS in the vascular system will block xylem vessels and disrupt water flow, causing wilt disease symptoms and eventually the death of infected plants (Genin and Deny, 2012). The internal symptoms are progressive discoloration of the vascular tissue in the early stages of infection, the disease develops in the pith and cortex, and then complete necrosis occurs. The external symptoms of infected plants are wilting, stunting, and yellowing of the foliage with the disease progression until the plant completely collapses (Àlvarez et al., 2010).
Rsi causes disease in a number of solanaceous plants and clove plants in Indonesia and other Asian countries (Safni et al., 2014). In Japan, Rsi strains have been isolated only from Solanum tuberosum (Horita et al., 2010), and showed varying levels of pathogenicity for tomato, groundnut, and tobacco. However, none of the strains tested were pathogenic for S. melongena (Suga et al., 2013). Rsi PW1001 is an RSSC phylotype IV biovar 2N that was isolated from potato plants in Japan and causes wilt disease on potato. However, the response of non-host plants to this pathogen has not been investigated so far. In this study, we found that inoculation of Rsi PW1001 into its non-host eggplant S. melongena cv. Senryo-nigou induced hypersensitive response (HR).
HR is a plant defense response to inoculation by pathogens, which is often accompanied by a rapid localized and programmed cell death; it restricts bacterial multiplication at the inoculation site and is associated with disease resistance (Balint-Kurti, 2019; Nakano and Mukaihara, 2019). Disease resistance (R) proteins have been evolved in plants to detect pathogen effectors inside plant cells during pathogen inoculation. The recognition of pathogen effectors by R proteins induces a strong defense response, called effector- triggered immunity (ETI), which includes ion effluxes, production of reactive oxygen species, phytohormone accumulation, and transcriptional activation of defense-related genes (Cui et al., 2015; Feys and Parker, 2000). Induction of the ETI response results in an HR, which is followed by elicitation by a pathogen or metabolite, electrolyte leakage due to membrane damage, the cessation of cyclosis, and cellular collapse (Balint-Kurti, 2019).
To induce HR, most bacterial pathogens require a type III secretion system (T3SS) to directly translocate some effectors into the plant cytoplasm. R. solanacearum injects approximately 70 effector proteins into host cells via the Hrp T3SS during infection (Mukaihara et al., 2010; Peeters et al., 2013). Nowadays, several effector proteins of R. solanacearum have been shown to act as avirulence determinants in certain plants. RipAA (formerly AvrA) triggers HR cell death and induces bacterial wilt resistance in Nicotiana tabacum (Carney and Denny, 1990). RipP1 (formerly PopP1), an acetyl-transferase effector of the YopJ family, restricts bacterial growth in Petunia St40 (Lavie et al., 2002). RipP2 (formerly PopP2) induces bacterial wilt resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana Nd-1 (Deslandes et al., 2003). RipP1 and RipAA from the R. solanacearum strain GMI1000 have been shown to act as avirulence determinants in N. tabacum and N. benthamiana (Poueymiro et al., 2009). RipAX2 (formerly Rip36) induces HR in the wild eggplant S. torvum (Nahar et al., 2014) and restricts the growth of R. solanacearum in eggplant AG91-25 (Morel et al., 2018). RipBN is recognized in tomato and induces resistance (Mazo-Molina et al., 2019). RipB is recognized as an Avr effector in N. benthamiana, N. tabacum, and N. otophora (Nakano and Mukaihara, 2019), and RipX (formerly PopA) and RipI are also reported as Avr effector in N. benthamiana (Sun et al., 2020; Zhuo et al., 2020). Furthermore, RipTPS which has trehalose-6-phosphate (T6P) synthase (TPS) has been reported to elicit HR-like response on tobacco (Poueymiro et al., 2014).
In this study, we investigated the involvement of trehalose in the interaction of bacterial pathogen and non-host plant. Trehalose is a non-reducing disaccharide consisting of two glucose molecules linked by α-1,1-glucosidic bond (Fernandez et al., 2010). Trehalose is synthesized in a two-step reaction from UDP-glucose (UDPG) and 6-phospho-glucose by TPS and trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase (TPP) (Miao et al., 2016). Bacteria have several trehalose synthesis pathways, including trehalose synthase (TreS), TreY/TreZ, and OtsA/OtsB pathways. The TreS pathway synthesizes trehalose from maltose using TreS, the TreY/ TreZ pathway synthesizes trehalose from maltooligosaccharides using maltooligosyl-trehalose synthase (TreY) and maltooligosyl-trehalose trehalohydrase (TreZ). In the OtsA/OtsB pathway, trehalose is synthesized from glucose-6-phosphate and UDPG, which is catalyzed by TPS (OtsA), then dephosphorylated by TPP (OtsB). MacIntyre et al. (2020) revealed that the OtsA/OtsB pathway is the predominant pathway for trehalose synthesis in R. solanacearum GMI1000. Rsi PW1001 also has an otsB/otsA gene cluster as an operon for trehalose synthesis in the OtsA/OtsB pathway.
Trehalose is a common metabolite that has been shown to be involved in conferring tolerance to a variety of environmental stresses, such as dehydration, heat, oxidative and osmotic stresses, and freezing (Hayner et al., 2017). Trehalose is also well-known player in biological signaling, development, and metabolic regulation (Lunn et al., 2014). Trehalose biosynthesis in some bacterial pathogens is also necessary for fitness and virulence, and has been an antibiotic target (Tournu et al., 2013). Despite comprehensive evidence of the biological benefits of trehalose in many organisms, relatively few reports about how trehalose and related metabolites function during plant-microbe interactions. Freeman et al. (2010) reported that mutating the treS and treY/Z pathways in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 decreased bacterial phyllosphere fitness in tomato leaves. In P. aeruginosa, trehalose is a key virulence factor to cause full disease symptoms on A. thaliana. Mutation of treS and treY/Z, genes for the synthesis pathway in P. aeruginosa, decreased the acquisition of nitrogen-containing nutrients and xyloglucan components of the plant cell wall, thereby inhibiting the replication of P. aeruginosa in intercellular spaces of leaves (Djonović et al., 2013). This evidence suggests that trehalose metabolism is required for bacterial movement into intercellular spaces and nitrogen uptake. Mutation of otsA/B in the trehalose synthesis pathway in Xanthomonas citri reduced virulence on citrus (Piazza et al., 2015). Furthermore, MacIntyre et al. (2020) generated ΔotsA and ΔtreY/treS/otsA in R. solanacearum GMI1000, and found that the level of disease index and bacterial propagation of these mutants on tomato were reduced, indicating that trehalose synthesis contributes to fitness and virulence.
However, the study of the role of trehalose synthesis for HR induction in plant-pathogen interaction has not been reported yet. Therefore, we mutated otsA and otsB in Rsi PW1001 and investigated trehalose concentration, effect on HR induction, and osmotic tolerance. The role of trehalose synthesis in the interaction of bacterial pathogen and plants will be discussed.
Eggplant (S. melongena cv. Senryo-nigou), wild eggplant S. torvum, and tobacco plants (N. tabacum cv. Xanthi) were grown in a growth chamber under the following conditions: a 16/8 h (light/dark) photoperiod at 28°C and 80% relative humidity, and 7-week-old plants were used for inoculation experiments.
The bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Tables 1 and 2. The strain Rsi PW1001 was spontaneously resistant to nalidixic acid (Nal) of MAFF327034 (Horita et al., 2010; Suga et al., 2013). Rsi PW1001 and R. pseudosolanacearum RS1002 strains were routinely cultured in BG medium (1% bacto peptone, 0.1% casamino acid, 0.1% yeast extract, and 0.5% glucose) at 27°C, and supplemented with antibiotics when needed (30-50 μg/ml of nalidixic acid, 30 μg/ml of kanamycin, 18 μg/ ml of tetracycline, or 30 μg/ml of gentamicin). Escherichia coli strains were routinely cultured in Luria-Bertani medium at 37°C and supplemented with appropriate antibiotics (100 μg/ml of ampicillin, 50 μg/ml of kanamycin, 30 μg/ ml of tetracycline, or 50 μg/ml of gentamicin).
To generate hrpB and hrcV mutants, parts of hrpB and hrcV fragments (0.8 kb) were amplified by PCR with primer pairs of P3747 and P3748 for hrpB, and P3749 and P3750 for hrcV. All primer sequences used in this study are listed in Supplementary Table 1. KOD-FX Neo DNA Polymerase (Toyobo Inc., Osaka, Japan) was used for all PCR for plasmid construction. Resulting PCR products were inserted into the plasmid pARO191 using an In-Fusion HD cloning kit (Takara, Shiga, Japan). Both resulting plasmids were transformed into E. coli S17-1 and integrated into wild-type (WT) of Rsi PW1001 by conjugation.
To generate ΔhpaB and ΔripTPS of Rsi PW1001, the hpaB and ripTPS coding region with their surrounding region was amplified with primer pairs of hpaB-F and hpaB-R for hpaB, and ripTPS-F and ripTPS-R for ripTPS, and inserted into a pGEM-T Easy vector (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). To delete the hpaB and ripTPS open reading frame, inverse PCR was performed with appropriate primer pairs, hpaB-d1, hpaB-d2, ripTPS-d1, and ripTPS-d2, respectively. Then, the PCR product was digested with XbaI and DpnI, and self-ligated with a Ligation-convenience kit (Nippon Gene, Tokyo, Japan). The ΔhpaB and ΔripTPS DNA construct was subcloned into pK18mobsacB at an EcoRI site (Schäfer et al., 1994) to obtain pK18-ΔhpaB and pK18-ΔripTPS, and transformed into E. coli S17-1. The ΔhpaB (PW1004) and ΔripTPS (PW1078) deletion mutants were generated by conjugation and homologous recombination with Rsi PW1001 WT. To confirm the precise deletion of target genes, colony PCR of the conjugants was carried out using the respective primer pair.
For construction of the otsA mutant in Rsi PW1001, a part of the otsA gene fragment (678 bp) was amplified by a primer pair of otsA-F_IF and otsA-R_IF and was inserted into the plasmid pARO191 using an In-Fusion HD cloning kit (Takara). A part of the otsB fragment (600 bp) of Rsi PW1001 was amplified with a primer pair, otsB-F_NEB and otsB-R_NEB, and inserted into the EcoRI site of pARO191 using NEBuilder Assembly (New England Biolabs, Tokyo, Japan). Both resulting plasmids were transformed into E. coli S17-1 and integrated into WT of Rsi PW1001. The homology of the DNA sequence of otsA between Rsi PW1001 and RS1002 was 93% identity. Therefore, to introduce mutation of otsA in RS1002, we integrated the plasmid pARO-otsA of Rsi PW1001 into WT strain RS1002, and generated otsA mutant RS1736. The mutants PW1005 (otsA::pARO), PW1006 (otsB::pARO), and RS1736 (otsA::pARO) were selected after conjugation on BG agar plates with 30 μg/ml of kanamycin and 30 μg/ ml of Nal, and the mutation of the surviving colonies was confirmed by PCR using primer otsA-1 and M13-R for otsA mutant, and otsB-1 and M13-R for otsB mutant.
For complementation of PW1005 and PW1006 in Rsi, the entire otsBA operon with its native promoter was amplified with primer pair (otsB-F and otsA-R), cloned into pGEM-T Easy and ligated with plasmid pBSL199 (Alexeyev and Shokolenko, 1995) at XbaI site. The resultant plasmid was transformed into E. coli S17-1 and introduced into PW1005 and PW1006 by conjugation. The complemented strains PW1007 and PW1008 were selected on BG plates with nalidixic acid and tetracycline.
For construction of the ripX::lacZ, a part of the ripX gene fragment and its promoter region (449 bp) was amplified by a primer pair of ripX-F and ripX-R and was inserted into the pGEM-T Easy vector (Promega) to generate pGEM-ripX-1. Then the ripX promoter fragment was excised by KpnI and NotI digestions, and was inserted into cohort vector pHRP315 (Parales and Harwood, 1993) at the same sites. A XbaI-EcoRI fragment containing the ripX from pHRP315-ripX was introduced into a broad host range lacZ transcriptional fusion vector, pHRP309 (Parales and Harwood, 1993) to obtain pHRP309-ripX. pHRP309-ripX was introduced into Rsi PW1001 WT and its derivative strains by conjugation and β-galactosidase assay was carried out.
To examine HR induction on non-host plant S. melongena cv. Senryo-nigou by Rsi PW1001 and on S. torvum and N. tabacum cv. Xanthi by RS1002, the infiltration was assayed as described by Mukaihara et al. (2004) with some modifications. The bacterial strains were cultured overnight in BG broth medium at 27°C, and the cells were harvested by centrifugation. The cell pellets were washed with 10 mM MgSO4, then adjusted the OD600 of 0.3 (ca. 3 × 108 cfu/ml). The bacterial suspensions were infiltrated into 7-week-old eggplant, tobacco, and wild eggplant leaves with a 1 ml needleless syringe. Infiltrated plants were incubated at 28°C, 80% humidity with 16/8 h photoperiod (light/dark) for 3 days, and HR was observed every 24 h. To investigate the effect of exogenous trehalose in HR induction, trehalose solution was added to bacterial suspensions at concentrations 0.25 mM or 2.5 mM, and infiltrated into 7-week-old eggplant leaves. HR development was observed for 3 days.
The severity of cell death in HR induction was quantified by the degree of electrolyte leakage from eggplant leaves. Leaf disks (8 mm in diameter) were collected from individual plants and immersed in 1 ml of water for 2 h at room temperature with gentle shaking, as previously described (Nakano et al., 2021). The ion conductivity of the water was measured using a conductivity meter (LAQUAtwin, Horiba, Kyoto, Japan).
For measurement of the trehalose concentration in Rsi PW1001 and its derivatives, the bacterial strains were grown overnight in 5 ml of minimal medium (50 mM KH2PO4, 7.6 mM (NH4)2SO4, 1.7 mM MgCl2, 1.7 mM NaCl at pH 7.0) at 27°C. Bacterial cells were harvested by centrifugation at 9,800 ×g for 10 min, the cell pellet was resuspended in 1 ml of distilled deionized water, and the cells were disrupted twice using a sonicator (Branson Sonifier, Danbury, CT, USA) at 40% duty cycle for 10 s with a 30 s interval in an ice bath. After sonication, disrupted cells were heated at 95°C for 10 min to inactivate trehalose-degrading enzymes, and the cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 9,800 ×g for 10 min (Li et al., 2012; MacIntyre et al., 2020).
The concentration of trehalose was determined by an enzymatic trehalose assay using a Trehalose Assay Kit (Megazyme, Wicklow, Ireland) in a microtube following the manual procedure. Briefly, 400 μl of distilled water, 40 μl of trehalose sample, 40 μl of solution 1 (buffer), 20 μl of solution 2 (NADP+, ATP), and 4 μl of suspension 3 (hexokinase/glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase) were added to the microtubes. Solutions were mixed and incubated for 5 min, then the absorbance values of a half volume of the solutions were read at 340 nm (A1) using UV-Vis Spectrophotometer UV mini 1240 (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). Subsequently, 2 μl of suspension 4 (trehalase) was added into the remaining volume of the solutions in the microtube, mixed, incubated for 8 min at room temperature, and the absorbance values were measured at 340 nm (A2). The amount of NADPH formed in this reaction is stoichiometric with the amount of d-glucose and thus with twice the amount of trehalose. The pre-existing glucose concentrations for both blank and sample were determined in a control reaction without trehalase (A1) and subtracted from the total glucose (A2). The trehalose concentration was calculated using Megazyme Mega-Calc per l of samples.
The β-galactosidase activity was measured as described by Miller (1992) with some modifications. The bacterial strains possessing pHRP309-ripX were cultured in the BG and minimal medium pH 7.0 at 27°C for 16 h, then bacterial densities were adjusted to OD595 of 0.2 in BG and minimal medium, and further incubated for 1 h. β-galactosidase activities were determined in 10 min reaction time and shown in Miller units.
To investigate effector translocation into plant cells Cya translocation assay system (Murata et al., 2006) was used, and ripX was selected as one of representative T3SS genes. For construction of the ripX::’cya fusion gene, a 1,324 bp DNA fragment of the promoter and entire ripX open reading frame without stop codon was amplified by a primer pair of ripX-F2 and ripX-R2 and cloned in pGEM-T Easy vector (Promega). The resultant plasmid, pGEM-ripX-2, was digested with XbaI and XhoI and then inserted into pARO-HA-’cya (Murata et al., 2006) to obtain pARO-ripX::’cya. Because both complemented strains are resistant to Nal, Km and Tet, we used Gm as a selection marker. A Gm-cassette was excised from pMS255 vector (Becker et al., 1995) by EcoRI digestion, and inserted into pARO-ripX::’ cya at EcoRI site to obtain pARO-ripX::’cya-Gm. This reporter plasmid was introduced into otsA and otsB mutant strains and otsA and otsB complemented strains. The resulting strains expressing ripX::’cya were used for in planta adenylate cyclase assay.
The in planta adenylate cyclase assay was performed as described by Murata et al. (2006) with some modifications. Briefly, bacterial strains expressing the ripX::’cya fusion gene were grown overnight in BG medium at 27°C. The bacterial cells were centrifuged, washed twice with distilled water, then resuspended at OD600 of 0.3. The bacterial suspension was infiltrated into 7-week-old eggplant leaves, then incubated at 28°C, 80% humidity with 16/8 h photoperiod (light/dark). After 15 h incubation, three-leaf disks (8 mm in diameter) from each sample were collected, frozen with liquid nitrogen, then ground with mortar and pestle. The leaf homogenates were boiled in 200 μl of 0.05 M sodium acetate buffer containing 0.02% bovine serum albumin for 5 min. Cell debris was removed by centrifugation twice for 10 min each, and the supernatant was collected in new microtubes and stored at −80°C until assayed for cAMP. The cAMP was measured using a Cyclic AMP EIA kit (Cayman Chemical Company, Ann Arbor, MI, USA).
Overnight cultures of Rsi PW1001 and derivatives were centrifugated, rinsed twice using BG fresh medium, and resuspended to OD600 of 0.05 (1 × 107 cfu/ml) in BG broth supplemented with or without 0.15 M NaCl or 10% sucrose in culture tubes. Tubes were incubated in a Bio-Shaker BR-21FP (Taitec, Kumagaya, Japan) at 27°C. The bacterial growth was measured using a CO7500 colorimeter (Biochrom, Holliston, MA, USA) at OD600 every 12 h for 72 h. Each experiment included two replicates per treatment from two independent experiments.
Statistical analyses were carried out using GraphPad Prism version 9 package (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). All results are expressed as means with standard deviation (SD). The data were analyzed by one-way/two-way ANOVA, and significant differences between means were calculated by Tukey’s multiple comparison test at P < 0.05 considered significant.
Rsi PW1001 is avirulent pathogen on eggplant. When we infiltrated it on eggplant at low cell density condition (OD600 = 0.0003), bacteria did not propagate and symptom did not appear even at 6 days post inoculation (dpi) (Supplementary Fig. 1). Although inoculation of WT strain PW1001 induced HR on eggplant Senryou-nigou, inoculation of hrpB and hrcV mutants abolished HR induction (Fig. 1A), indicating the importance of T3SS in HR induction. Furthermore, the ΔhpaB mutant also abolished HR induction, indicating T3SS-dependent effector transfer was required for HR. To investigate the role of trehalose biosynthesis in HR induction by Rsi PW1001 on eggplant S. melongena cv. Senryonigou, we generated otsA and otsB gene-disrupted mutants and their complemented strains and infiltrated these bacteria into the eggplant leaves. WT strain PW1001 caused HR at 2-3 dpi, whereas both mutants of otsA (PW1005) and otsB (PW1006) abolished HR induction to the level of hrp mutants (Fig. 1). The introduction of intact otsBA into the otsA and otsB mutants completely restored the development of HR. HR cell death on infiltrated leaves was accompanied by electrolyte leakage. We measured the degree of ion leakage from the leaf disks at 2 and 3 dpi. As expected, the otsA and otsB mutants had significantly reduced ion leakage compared to the WT (Fig. 1B), suggesting that trehalose biosynthesis might be required for HR induction on eggplant by Rsi PW1001.
We investigated the potential involvement of RipTPS in Rsi PW1001-induced HR on eggplant. However, infiltration of ΔripTPS still induced HR-like WT on eggplant at 2-3 dpi (Fig. 1C), and the degree of ion leakage was also similar to the WT (Fig. 1D). This result suggests that RipTPS is not involved in Rsi PW1001-induced HR in eggplant, although both OtsA and RipTPS encode TPS in the trehalose biosynthesis pathway.
To investigate the effect of exogenous trehalose on HR induction in eggplant, we added trehalose at two concentrations (0.25 mM and 2.5 mM) to the bacterial cultures. We observed that infiltration with only trehalose, both at 0.25 and 2.5 mM, did not induce HR. Although WT strain PW1001 induced HR, otsA and otsB mutants did not induce it, like the WT strain (Fig. 2A). The addition of exogenous trehalose to the WT strain did not affect HR induction, and addition to the otsA and otsB mutants did not restore HR. To confirm that exogenous trehalose did not affect the HR level, we measured ion leakage from the infiltrated leaves. The otsA and otsB mutants had significantly reduced ion leakage, even with trehalose as compared to the WT (Fig. 2B). Namely, exogenous trehalose did not affect the ion leakage in infiltrated eggplant leaves.
To confirm that otsA and otsB mutants reduced the ability to synthesize trehalose, we used a Trehalose Assay Kit to quantify the trehalose concentration in the bacterial cells (Fig. 3). Both mutant strains had significantly reduced trehalose concentrations compared to WT. The trehalose concentration of WT strain PW1001, otsA mutant, and otsB mutant was 73.8, 13.3, and 6.5 mg/l of each trehalose sample, respectively. The complemented strains of otsA and otsB completely recovered their ability to synthesize trehalose; moreover, the trehalose concentration was higher than in the WT strain. The trehalose concentrations of complemented strains of otsA and otsB were 121.0 and 147.0 mg/l of each trehalose sample. In this study, we found that Rsi PW1001 does not export trehalose extracellularly because there was almost no trehalose in the spent media (Supplementary Fig. 2).
To investigate whether trehalose biosynthesis affects T3SS gene expression, the effector gene ripX expression was investigated as a representative T3SS gene. The expression of ripX is known to be under the control of HrpB (Sun et al., 2020). We measured β-galactosidase activity of the bacterial strains possessing ripX::lacZ in BG and minimal medium. As shown in Fig. 4, the β-galactosidase activity in BG medium was lower than in minimal medium, suggesting that ripX gene expression was induced in minimal medium. However, there was no significant difference in the β-galatosidase activities between WT, otsA, and otsB mutants, and their complemented strains. In addition, an effector translocation study using ripX::’cya construct in otsA and otsB mutants, and their complemented strains was conducted. The cAMP was low without ripX::’cya, but significant amount of cAMP was detected with ripX::’cya in all strains. However, there is no significant difference among the strains (Supplementary Fig. 3). These results indicate that expression of ripX and probably other T3SS genes and RipX translocation to eggplant is likely independent on trehalose biosynthesis of Rsi.
To determine if trehalose biosynthesis contributes to tolerance of osmotic stress in Rsi PW1001, we measured the bacterial growth of WT, otsA and otsB mutants, and their complemented strains in BG medium supplemented with/without 0.15 M NaCl or 10% sucrose at 27°C for 36 h and 60 h. There was no significant difference in the bacterial growth between WT, otsA and otsB mutants, and their complemented strains in BG medium without NaCl (Fig. 5A) nor sucrose (Fig. 5B). However, both mutant strains had lower growth than WT under osmotic stress conditions, both with NaCl (Fig. 5A) or sucrose (Fig. 5B), and complemented strains partially with NaCl and almost completely with sucrose restored their growth. These results indicate that Rsi PW1001 requires trehalose biosynthesis for full osmotic stress tolerance.
In order to investigate whether trehalose synthesis is required for HR induction in other strains of RSSC, we generated an otsA mutant in R. pseudosolanacearum RS1002 and confirmed that otsA mutant strain, RS1736 also significantly reduced the trehalose concentration compared to WT RS1002 (Supplementary Fig. 4). However, we observed that the RS1736, otsA mutant of RS1002 induced HR-like WT at 2 dpi, both on wild eggplant S. torvum and tobacco N. tabacum (Fig. 6). This result indicates that the involvement of trehalose synthesis for HR induction is not common in RSSC.
Trehalose is a non-reducing disaccharide found in many organisms, including bacteria, fungi, insects, and plants, and plays a wide range of functional and structural roles. Currently, there are five known trehalose biosynthetic routes, and the OtsA/OtsB pathway is the most widespread pathway in prokaryotes and eukaryotes (Paul et al., 2008). This pathway produces the intermediate T6P, which is an important key signal molecule in plantpathogenic bacteria interactions and affects many metabolic pathways, developmental processes, and stress responses (Lunn et al., 2014). Several studies also revealed the role of T6P in regulation of carbon assimilation and the sugar status in plants (Paul et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2009).
Poueymiro et al. (2014) reported that R. solanacearum encodes RipTPS, a type III-secreted effector that is a functional TPS, in addition to OtsA. RipTPS is translocated into plant cells by T3SS, and elicits HR in N. tabacum. This finding proposed speculation that the pathogen directly induces T6P synthesis during the course of infection to subvert plant cell metabolism through the endogenous T6P concentration in the plant rather than to stimulate trehalose biosynthesis. However, the involvement of RipTPS in compatible interactions was not revealed yet. In line with this function of RipTPS, we found that ΔripTPS mutant Rsi PW1078 did not abolish HR and ion leakage on eggplant compared to WT (Fig. 1C and D), indicating that RipTPS is not avirulence factor in eggplant.
In this study, we provided evidence that trehalose biosynthesis in Rsi PW1001 is required for HR induction on eggplant because mutation of otsA and otsB significantly reduced HR level (Fig. 1). However, T3SS is indispensable for HR induction because the hrpB, hrcV, and ΔhpaB mutants abolished HR. The hrpB, hrcV, and hpaB genes are required for the expression T3SS genes, biogenesis of Hrp pili and the translocation of the T3Es into the host cells (Asolkar and Ramesh, 2018; Lonjon et al., 2016; Mukaihara et al., 2004). Thus, a T3SS-dependent effector may induce HR. However, trehalose biosynthesis does not appear to affect T3SS gene the expression or T3Es translocation. The ripX is a representative effector gene in RSSC and RipX induces HR on tobacco plants (Sun et al., 2020). We observed that the β-galactosidase activities of all bacterial strains possessing ripX::lacZ were not significantly different in a minimal medium, suggesting that trehalose biosynthesis did not affect ripX expression. This finding suggests that trehalose biosynthesis might have no effect for hrpB-dependent effector gene expression. There might be a novel effector present in Rsi strains to induce HR on eggplant, whose expression is hrpB-independent and requires trehalose biosynthesis in Rsi. However, this effector still requires Hrp-apparatus for its secretion and translocation.
The addition of exogenous trehalose to the bacterial culture did not affect the HR level or ion leakage in the infiltrated eggplant leaves. Infiltration of trehalose alone also did not induce HR and ion leakage (Fig. 2). In contrast, it is reported that application of exogenous trehalose induced resistance to the biotrophic fungus Blumeria graminis, which causes powdery mildew in wheat (Tayeh et al., 2014) and triggers plant defense responses in citrus leaves (Piazza et al., 2015).
Based on the results, we conclude that only intracellular trehalose was involved in HR induction of eggplant by Rsi PW1001. This conclusion was further supported by measurement of the trehalose concentration in the bacterial cells. We observed low intracellular trehalose concentrations in the otsA and otsB mutants. This finding is in agreement with a previous study revealing the intracellular localization of trehalose in R. solanacearum GMI1000 (MacIntyre et al., 2020). In that study, they measured the trehalose concentration by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis, and trehalose was not detected in spent cell media, suggesting that R. solanacearum does not export trehalose extracellularly. Thus, trehalose biosynthesis-defective mutants in R. solanacerum GMI1000 showed reduced in planta multiplication in host tomato plant and disease incidence (MacIntyre et al., 2020). Unlike this observation, although trehalose is required for virulence toward Arabidopsis leaves, extracellular trehalose was important in P. aeruginosa PA14 (Djonović et al., 2013). The P. aeruginosa PA14 ΔtreYZΔtreS mutant reduced in planta growth, while application of exogenous trehalose restored bacterial growth in a dose-dependent manner (Djonović et al., 2013). The role of trehalose in plant-pathogen interactions appears to depend on the type of pathogen.
Trehalose accumulation in intracellular spaces functions as a compatible solute to contend with osmotic stress to an equilibrium at which water no longer moves out of the cell into high osmolarity environments (Argüelles, 2000; Csonka, 1989). In line with this function, we found that the otsA and otsB mutants showed lower growth than WT in BG medium supplemented with 0.15 M NaCl or 10% sucrose. This evidence suggests that trehalose has important role as an osmoprotectant. Compatible solutes like trehalose could help this soilborne pathogen survive in an osmotically stressful environment (van Elsas et al., 2001). Rsi may experience hyperosmolarity in plant xylem vessels during infection. In this study, although we attempted to generate deletion mutants of otsA and otsB using the sucrose-sensitive suicide vector pK18mobSacB (Schäfer et al., 1994), we obtained only WT strains after 10% sucrose selection. This result suggests that high concentration of sucrose could be an osmotic stress factor and affect the multiplication of trehalose-deficient strains.
In contrast to the effect of the HR phenotype of the otsA mutant Rsi PW1005 on eggplant S. melongena cv. Senryo-nigou, RS1736, a mutant of otsA in RS1002 strain induced HR-like the WT on its non-host plants, wild eggplant and tobacco plant (Fig. 6). Because otsA mutant of RS1002 still induced HR on wild eggplant and tobacco, trehalose biosynthesis is not required for HR induction, and defect of trehalose biosynthesis probably did not interfere T3SS gene expression. On the other hand, trehalose-defective mutants in Rsi reduced HR on eggplant, suggesting that the gene expression of particular effector that could induce HR might be affected by trehalose biosynthesis.
Electronic Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material is available at The Plant Pathology Journal website (http://www.ppjonline.org/).
Fig. 1
Hypersensitive response (HR) on eggplant Solanum melongena cv. Senryo-nigou. (A, C) HR in leaves inoculated with the bacterial suspension (OD600 of 0.3) of Ralstonia syzygii subsp. indonesiensis PW1001 (WT), PW1002 (hrpB), PW1003 (hrcV), PW1004 (ΔhpaB), PW1005 (otsA), PW1006 (otsB), the complemented strains PW1007 (otsA TnotsBA+) and PW1008 (otsB TnotsBA+), PW1078 (ΔripTPS), and 10 mM MgSO4 (Mock). Photographs show representative results from three independent experiments with similar results at 2 and 3 dpi. (B, D) The degree of ion leakage from strain-infiltrated eggplant leaves was measured at 3 dpi using a conductivity meter. Values are means ± SD of two replicates from two independent experiments. Different letters indicate significant differences among the nine inoculations (B) and six inoculations (D) as defined by Tukey’s multiple comparison test (P < 0.05).

Fig. 2
The effect of exogenous trehalose in Ralstonia syzygii subsp. indonesiensis (Rsi)-induced hypersensitive response of eggplant Solanum melongena cv. Senryo-nigou. (A) Leaves were infiltrated with the bacterial suspension (OD600 of 0.3) of Rsi PW1001 (WT), PW1005 (otsA), or PW1006 (otsB) and without exogenous trehalose or with trehalose at 0.25 mM (T1) and 2.5 mM (T2) final concentrations. Photographs were taken at 3 dpi from three independent experiments with similar results; representative results are shown. (B) The degree of ion leakage from leaves was measured at 3 dpi using a conductivity meter. Values are means ± SD of two replicates from two independent experiments. Different letters indicate significant differences among the four inoculations as defined by Tukey’s multiple comparison test (P < 0.05).
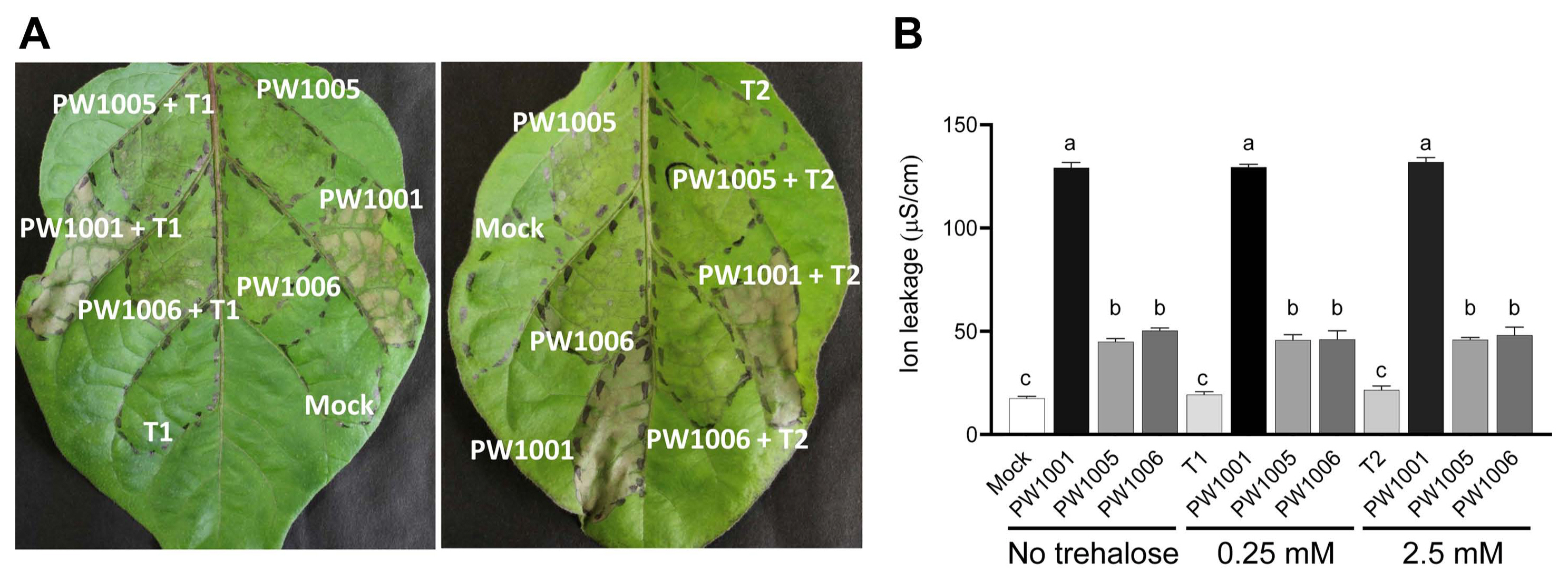
Fig. 3
Trehalose concentration of trehalose samples prepared from bacterial cells that were cultured in minimal medium for 16 h. The trehalose concentration was measured using a Trehalose Assay Kit. Values are means ± SD of four replicates. Different letters indicate significant differences among the five strains as defined by Tukey’s multiple comparison test (P < 0.05).
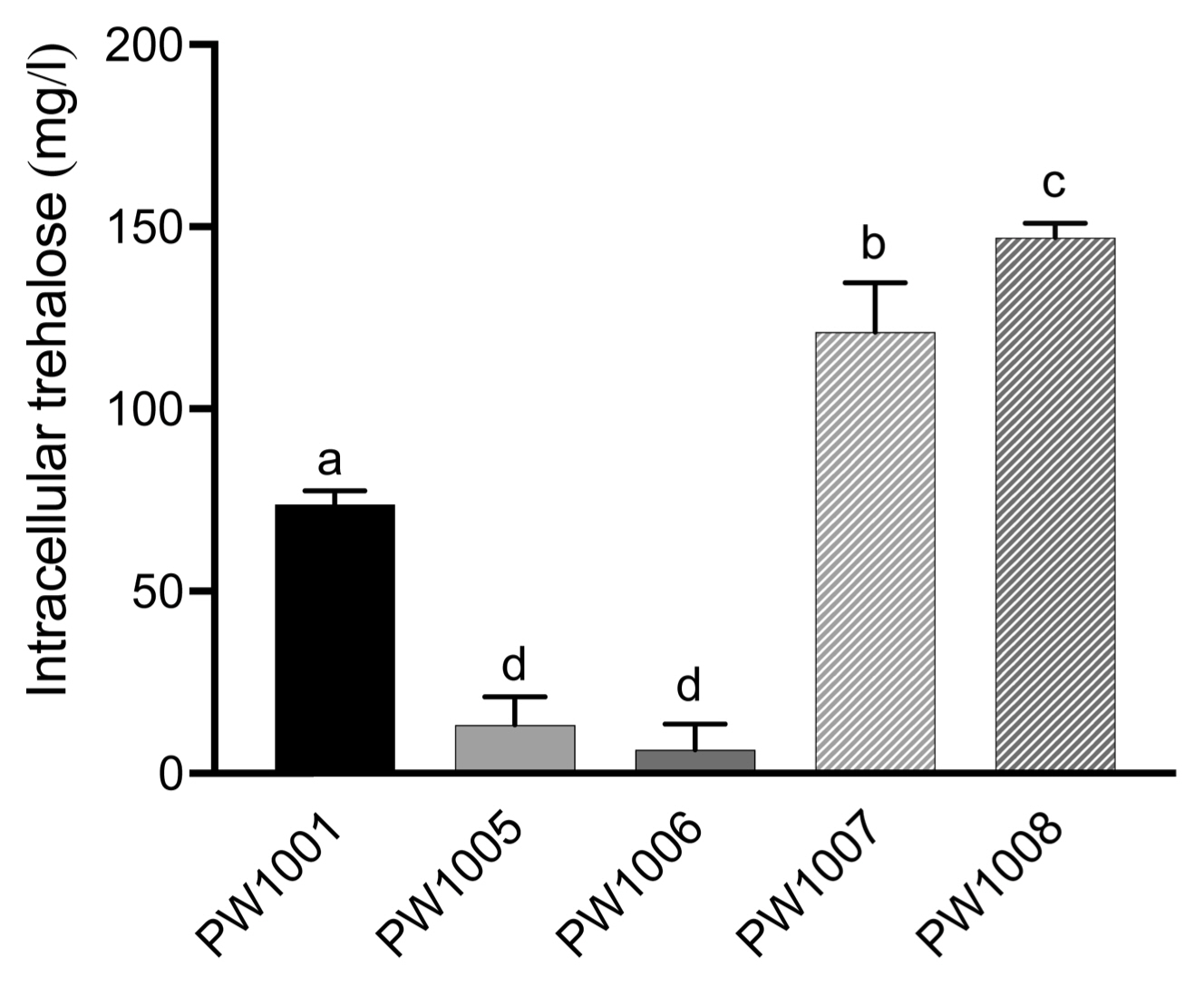
Fig. 4
Gene expression of ripX. The ripX gene expression in Ralstonia syzygii subsp. indonesiensis (Rsi) PW1079 (WT), PW1080 (otsA), PW1081 (otsB), the complemented strains PW1082 (otsA TnotsBA+) and PW1083 (otsB TnotsBA+). The ripX promoter was fused to the lacZ gene, and the effect of trehalose biosynthesis on β-galactosidase activity in Rsi PW1079 and its derivative strains was examined. The β-galactosidase activities are indicated as Miller units. Values are means ± SD of four replicates from two independent experiments. Different letters indicate significant differences among the five strains as defined by Tukey’s multiple comparison test (P < 0.05).
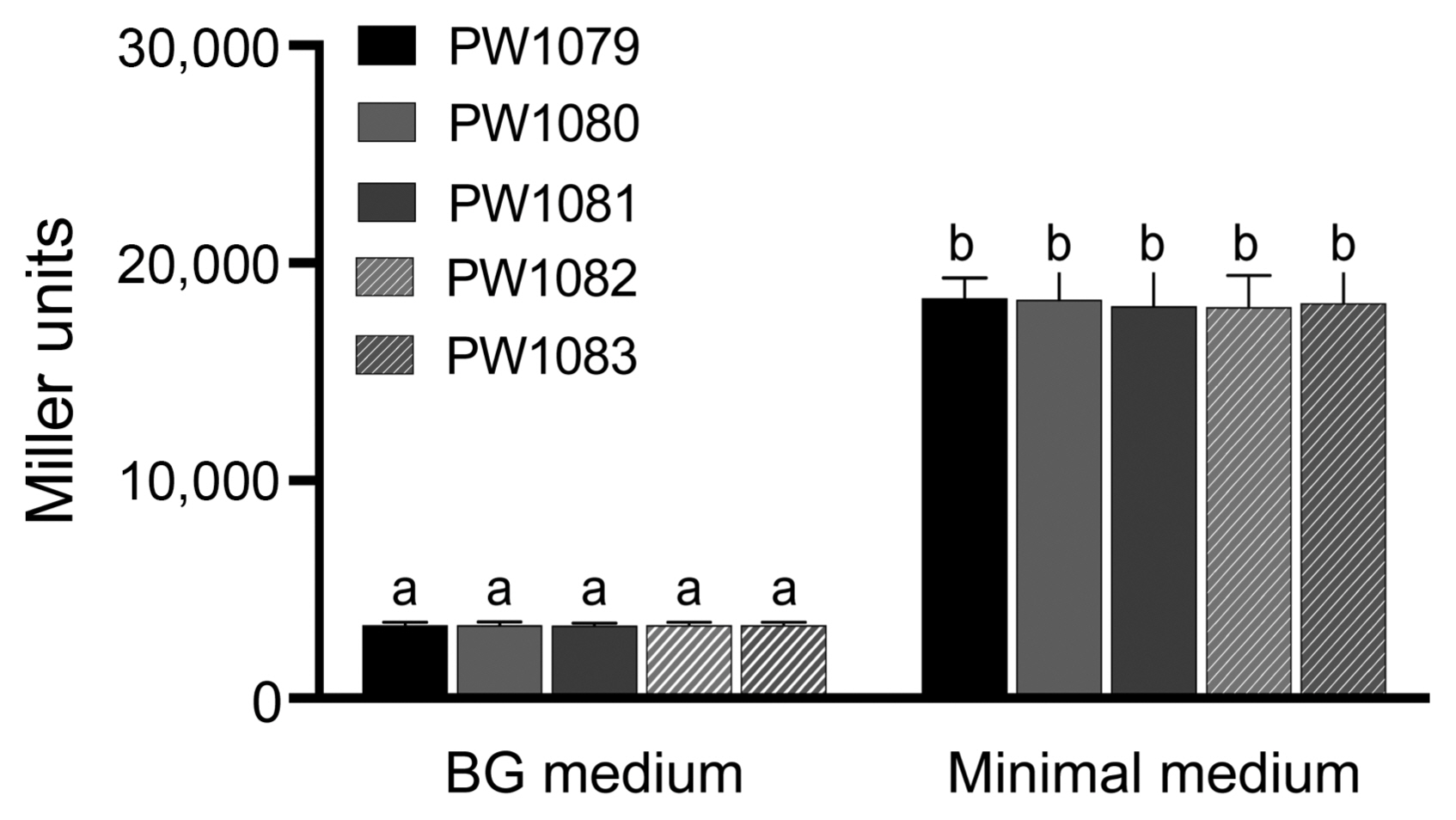
Fig. 5
Trehalose biosynthesis is required for Ralstonia syzygii subsp. indonesiensis PW1001 osmotic stress tolerance, either in NaCl or sucrose. (A) The bacterial growth in each strain in BG medium with/without 0.15 M NaCl at 36 h and 60 h incubation time. (B) The bacterial growth in each strain in BG medium with/without 10% sucrose at 36 h and 60 h incubation time. Values are means ± SD of two replicates from two independent experiments. Different letters indicate significant differences among different conditions of five strains as defined by Tukey’s multiple comparison test (P < 0.05).

Fig. 6
Hypersensitive response (HR) on wild eggplant Solanum torvum (A, B) and tobacco Nicotiana tabacum cv. Xanthi (C, D) by infiltration of Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum RS1002 and its derivatives. (A) HR on wild eggplant leaf inoculated with RS1002 (WT), RS1211 (hpaB), RS1273 (ΔhrpY), RS1662 (ΔripAX2), RS1736 (otsA), and 10 mM MgSO4 (mock) at 2 dpi. (B) The degree of ion leakage from wild eggplant leaves was measured at 2 dpi. (C) HR on tobacco leaf inoculated with R. pseudosolanacearum RS1002 (WT), RS1211 (ΔhpaB), RS1273 (ΔhrpY), RS1736 (otsA), and 10 mM MgSO4 (mock) at 3 dpi. (D) The degree of ion leakage from tobacco leaves was measured at 3 dpi. Values are means ± SD of two replicates from three independent experiments with similar results and representative results are shown. Different letters indicate significant differences among the six (B) and five (D) inoculations as defined by Tukey’s multiple comparison test (P < 0.05).
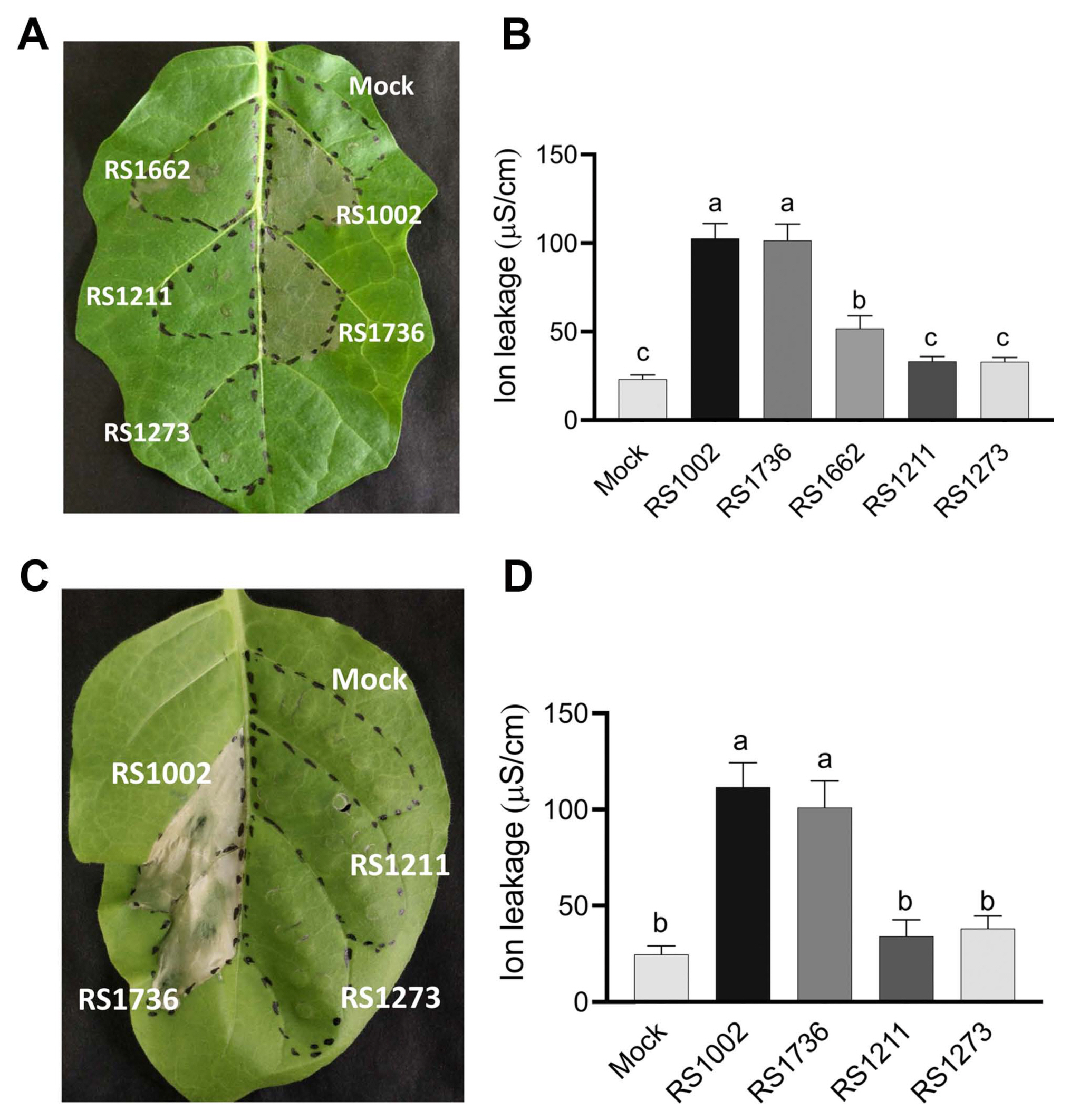
Table 1
Bacterial strains used in this study
| Bacterial strain | Relevant characteristics | Reference or source |
|---|---|---|
| Ralstonia syzygii subsp. indonesiensis | ||
| PW1001 | Spontaneously resistant strain to nalidixic acid of MAFF327034 | This study |
| PW1002 | PW1001 hrpB::pARO (Nalr and Kmr) | This study |
| PW1003 | PW1001 hrcV::pARO (Nalr and Kmr) | This study |
| PW1004 | PW1001 ΔhpaB (Nalr) | This study |
| PW1005 | PW1001 otsA::pARO (Nalr and Kmr) | This study |
| PW1006 | PW1001 otsB::pARO (Nalr and Kmr) | This study |
| PW1007 | PW1001 otsA::pARO chr::miniTn10 otsBA (Nalr, Kmr and Tetr) | This study |
| PW1008 | PW1001 otsB::pARO chr::miniTn10 otsBA (Nalr, Kmr and Tetr) | This study |
| PW1078 | PW1001 ΔripTPS (Nalr) | This study |
| PW1079 | PW1001 possessing ripX::lacZ (Nalr and Gmr) | This study |
| PW1080 | PW1005 possessing ripX::lacZ (Nalr and Gmr) | This study |
| PW1081 | PW1006 possessing ripX::lacZ (Nalr and Gmr) | This study |
| PW1082 | PW1007 possessing ripX::lacZ (Nalr and Gmr) | This study |
| PW1083 | PW1008 possessing ripX::lacZ (Nalr and Gmr) | This study |
| PW1085 | PW1005 ripX::’cya (expressing RipX-’Cya, Nalr and Gmr) | This study |
| PW1086 | PW1006 ripX::’cya (expressing RipX-’Cya, Nalr and Gmr) | This study |
| PW1087 | PW1007 ripX::’cya (expressing RipX-’Cya, Nalr and Gmr) | This study |
| PW1088 | PW1008 ripX::’cya (expressing RipX-’Cya, Nalr and Gmr) | This study |
| R. pseudosolanacearum | ||
| RS1002 | RS1000 (Nalr) | Mukaihara et al. (2004) |
| RS1211 | RS1002 ΔhpaB (Nalr) | Mukaihara et al. (2004) |
| RS1273 | RS1002 ΔhrpY (Nalr) | Mukaihara et al. (2004) |
| RS1662 | RS1002 ΔripAX2 (Nalr) | Nahar et al. (2014) |
| RS1736 | RS1002 otsA::pARO (Nalr and Kmr) | This study |
| Escherichia coli | ||
| DH5α | F−, λ−, ø80dLacZΔM15, Δ(lacZYA-argF)U169, recA1, endA1, hsdR17(rK−mK+), supE44, thi-1, gyrA, relA1 | Nippon Gene |
| S17-1 | Thi pro hsdR-hsdM + recA [chr::RP4-2-Tc::Mu-Km::Tn7] | Schäfer et al. (1994) |
| S17-1 | λpir λpir lysogeny of S17-1 | Simon et al. (1983) |
Table 2
Plasmids used in this study
| Plasmid | Relevant characteristics | Reference or source |
|---|---|---|
| pGEM-T Easy | Cloning vector for PCR product, Ampr | Promega |
| pGEM-otsBA | pGEM-T Easy carrying 3006 bp PCR product with otsBA with their native promoter from PW1001, Ampr | This study |
| pGEM-hpaB | pGEM-T Easy carrying 1911 bp PCR product with hpaB with its native promoter from PW1001, Ampr | This study |
| pGEM-ripTPS | pGEM-T Easy carrying 2958 bp PCR product with ripTPS with its native promoter from PW1001, Ampr | This study |
| pGEM-ripX-1 | pGEM-T Easy carrying 449 bp PCR product with ripX with its native promoter from PW1001, Ampr | This study |
| pGEM-ripX-2 | pGEM-T Easy carrying 1324 bp PCR product with ripX with its native promoter from PW1001, Ampr | This study |
| pK18mobsacB | Small mobilizable vector, sucrose-sensitive (sacB), Kmr | Schäfer et al. (1994) |
| pK18mobsacB-ΔhpaB | pK18mobsacB with upstream and downstream regions of hpaB, Kmr | This study |
| pK18mobsacB-ΔripTPS | pK18mobsacB with upstream and downstream regions of ripTPS, Kmr | This study |
| pARO191 | The mobilizable narrow-host-range vector derived from pUC19, Kmr | Parke (1990) |
| pARO191-hrpB | pARO191 containing 0.8 kb hrpB-DNA fragment from PW1001, Kmr | This study |
| pARO191-hrcV | pARO191 containing 0.8 kb hrcV-DNA fragment from PW1001, Kmr | This study |
| pARO191-otsA | pARO191 containing 678 bp otsA-DNA fragment from PW1001, Kmr | This study |
| pARO191-otsB | pARO191 containing 600 bp otsB-DNA fragment from PW1001, Kmr | This study |
| pARO-HA-’cya | Cya reporter plasmid, Kmr | Murata et al. (2006) |
| pARO-ripX::’cya | pARO-HA-’cya containing 1324 bp of ripX fragment and its promoter region at XbaI and XhoI sites, Kmr | This study |
| pBSL199 | Mini-Tn10 transposon vector derived from pBSL177, Ampr, Tetr | Alexeyev and Shokolenko (1995) |
| pBSL199-otsBA | pBSL199 connecting with pGEM-otsBA at XbaI site, Ampr, Tetr | This study |
| pHRP315 | Cohort vector for directed cloning of promoter fragment, Ampr | Parales and Harwood (1993) |
| pHRP315-ripX | pHRP315 containing 449 bp ripX-DNA fragment and its promoter region at KpnI and NotI sites, Ampr | This study |
| pHRP309 | Broad-host-range lacZ transcriptional fusion vector based on the IncQ plasmid RSF1010, Gmr | Parales and Harwood (1993) |
| pHRP309-ripX | pHRP309 possessing XbaI-EcoRI fragment of pHRP315-ripX, ripX-lacZ transcriptional fusion vector, Gmr | This study |
| pMS255 | Vector containing Gentamicin-cassette, Gmr, Ampr | Becker et al. (1995) |
| pARO-ripX::’cya-Gm | pARO-ripX::’cya with Gm-cassette from pMS255 at EcoRI site, Kmr, Gmr | This study |
References
Alexeyev, MF and Shokolenko, IN 1995. Mini-Tn10 transposon derivatives for insertion mutagenesis and gene delivery into the chromosome of gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 160:59-62.


Àlvarez, B, Biosca, EG and López, MM 2010. On the life of Ralstonia solanacearum, a destructive bacterial plant pathogen. In: Current research, technology and education topics in applied microbiology and microbial biotechnology, eds. by A Méndez-Vilas, 267-279. Formatex Research Center, Badajoz, Spain.
Argüelles, JC 2000. Physiological roles of trehalose in bacteria and yeasts: a comparative analysis. Arch Microbiol. 174:217-224.


Asolkar, T and Ramesh, R 2018. Development of T3SS mutants (hrpB
−
and hrcV
−
) of Ralstonia solanacearum, evaluation of virulence attenuation in brinjal and tomato: a pre-requisite to validate T3Es of R. solanacearum
. Indian J Microbiol. 58:372-380.



Balint-Kurti, P 2019. The plant hypersensitive response: concepts, control and consequences. Mol Plant Pathol. 20:1163-1178.



Becker, A, Schmidt, M, Jäger, W and Pühler, A 1995. New gentamicin-resistance and lacZ promoter-probe cassettes suitable for insertion mutagenesis and generation of transcriptional fusions. Gene. 162:37-39.


Carney, BF and Denny, TP 1990. A cloned avirulence gene from Pseudomonas solanacearum determines incompatibility on Nicotiana tabacum at the host species level. J Bacteriol. 172:4836-4843.



Csonka, LN 1989. Physiological and genetic responses of bacteria to osmotic stress. Microbiol Rev. 53:121-147.



Cui, H, Tsuda, K and Parker, JE 2015. Effector-triggered immunity: from pathogen perception to robust defense. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 66:487-511.


Deslandes, L, Olivier, J, Peeters, N, Feng, DX, Khounlotham, M, Boucher, C, Somssich, I, Genin, S and Marco, Y 2003. Physical interaction between RSS1-R, a protein conferring resistance to bacterial wilt, and PopP2, a type III effector targeted to the plant nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 100:8024-8029.



Djonović, S, Urbach, JM, Drenkard, E, Bush, J, Feinbaum, R, Ausubel, JL, Traficante, D, Risech, M, Kocks, C, Fischbach, MA, Priebe, GP and Ausubel, FM 2013. Trehalose biosynthesis promotes Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenicity in plants. PLoS Pathog. 9:e1003217.



Du, H, Chen, B, Zhang, X, Zhang, F, Miller, SA, Rajashekara, G, Xu, X and Geng, S 2017. Evaluation of Ralstonia solanacearum infection dynamics in resistant and susceptible pepper lines using bioluminescence imaging. Plant Dis. 101:272-278.


Fernandez, O, Béthencourt, L, Quero, A, Sangwan, RS and Clément, C 2010. Trehalose and plant stress responses: friend or foe? Trends Plant Sci. 15:409-417.


Feys, BJ and Parker, JE 2000. Interplay of signaling pathways in plant disease resistance. Trends Genet. 16:449-455.


Freeman, BC, Chen, C and Beattie, GA 2010. Identification of the trehalose biosynthetic loci of Pseudomonas syringae and their contribution to fitness in the phyllosphere. Environ Microbiol. 12:1486-1497.


Genin, S 2010. Molecular traits controlling host range and adaptation to plants in Ralstonia solanacearum
. New Phytol. 187:920-928.


Genin, S and Deny, TP 2012. Pathogenomics of the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 50:67-89.


Hayner, GA, Khetan, S and Paulick, MG 2017. Quantification of the disaccharide trehalose from biological samples: a comparison of analytical methods. ACS Omega. 2:5813-5823.



Horita, M, Suga, Y, Ooshiro, A and Tsuchiya, K 2010. Analysis of genetic and biological characters of Japanese potato strains of Ralstonia solanacearum
. J Gen Plant Pathol. 76:196-207.

Lavie, M, Shillington, E, Eguiluz, C, Grimsley, N and Boucher, C 2002. PopP1, a new member of the YopJ/AvrRxv family of type III effector proteins, acts as a host-specificity factor and modulates aggressiveness of Ralstonia solanacearum
. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 15:1058-1068.


Li, H, Su, H, Kim, SB, Chang, YK, Hong, S-K, Seo, Y-G and Kim, C-J 2012. Enhanced production of trehalose in Escherichia coli by homologous expression of otsBA in the presence of the trehalase inhibitor, validamycin A, at high osmolarity. J Biosci Bioeng. 113:224-232.


Lonjon, F, Turner, M, Henry, C, Rengel, D, Lohou, D, van de Kerkhove, Q, Cazalé, A-C, Peeters, N, Genin, S and Vailleau, F 2016. Comparative secretome analysis of Ralstonia solanacearum type 3 secretion-associated mutants reveals a fine control of effector delivery, essential for bacterial pathogenicity. Mol Cell Proteomics. 15:598-613.


Lunn, JE, Delorge, I, Figueroa, CM, Van Dijck, P and Stitt, M 2014. Trehalose metabolism in plants. Plant J. 79:544-567.


MacIntyre, AM, Barth, JX, Pellitteri Hahn, MC, Scarlett, CO, Genin, S and Allen, C 2020. Trehalose synthesis contributes to osmotic stress tolerance and virulence of the bacterial wilt pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum
. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 33:462-473.


Mansfield, J, Genin, S, Magori, S, Citovsky, V, Sriariyanum, M, Ronald, P, Dow, M, Verdier, V, Beer, SV, Machado, MA, Toth, I, Salmond, G and Foster, GD 2012. Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol. 13:614-629.



Mazo-Molina, C, Mainiero, S, Hind, SR, Kraus, CM, Vachev, M, Maviane-Macia, F, Lindeberg, M, Saha, S, Strickler, SR, Feder, A, Giovannoni, JJ, Smart, CD, Peeters, N and Martin, GB 2019. The Ptr1 locus of Solanum lycopersicoides confers resistance to race 1 strains of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato and to Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum by recognizing the type III effectors AvrRpt2 and RipBN. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 32:949-960.


Meng, F 2013. The virulence factors of the bacterial wilt pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum
. J Plant Pathol Microbiol. 4:168.

Miao, Y, Tenor, JL, Toffaletti, DL, Washington, EJ, Liu, J, Shadrick, WR, Schumacher, MA, Lee, RE, Perfect, JR and Brennan, RG 2016. Structures of trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase from pathogenic fungi reveal the mechanisms of substrate recognition and catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 113:7148-7153.



Miller, JH 1992. The lac system. In: A short course in bacterial genetics: a laboratory manual and handbook for Escherichia coli and related bacteria, eds. by JH Miller, 43-80. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, NY, USA.
Minh Tran, T, MacIntyre, A, Khokhani, D, Hawes, M and Allen, C 2016. Extracellular DNases of Ralstonia solanacearum modulate biofilms and facilitate bacterial wilt virulence. Environ Microbiol. 18:4103-4117.


Morel, A, Guinard, J, Lonjon, F, Sujeeun, L, Barberis, P, Genin, S, Vailleau, F, Daunay, M-C, Dintinger, J, Poussier, S, Peeters, N and Wicker, E 2018. The eggplant AG91-25 recognizes the Type III-secreted effector RipAX2 to trigger resistance to bacterial wilt (Ralstonia solanacearum species complex). Mol Plant Pathol. 19:2459-2472.



Mori, Y, Inoue, K, Ikeda, K, Nakayashiki, H, Higashimoto, C, Ohnishi, K, Kiba, A and Hikichi, Y 2016. The vascular plant-pathogenic bacterium Ralstonia solanacearum produces biofilms required for its virulence on the surfaces of tomato cells adjacent to intercellular spaces. Mol Plant Pathol. 17:890-902.



Mukaihara, T, Tamura, N and Iwabuchi, M 2010. Genome-wide identification of a large repertoire of Ralstonia solanacearum type III effector proteins by a new functional screen. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 23:251-262.


Mukaihara, T, Tamura, N, Murata, Y and Iwabuchi, M 2004. Genetic screening of Hrp type III-related pathogenicity genes controlled by the HrpB transcriptional activator in Ralstonia solanacearum
. Mol Microbiol. 54:863-875.


Murata, Y, Tamura, N, Nakaho, K and Mukaihara, T 2006. Mutations in the lrpE gene of Ralstonia solanacearum affects Hrp pili production and virulence. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 19:884-895.


Nahar, K, Matsumoto, I, Taguchi, F, Inagaki, Y, Yamamoto, M, Toyoda, K, Shiraishi, T, Ichinose, Y and Mukaihara, T 2014.
Ralstonia solanacearum type III secretion system effector Rip36 induces a hypersensitive response in the nonhost wild eggplant Solanum torvum
. Mol Plant Pathol. 15:297-303.


Nakano, M, Ichinose, Y and Mukaihara, T 2021.
Ralstonia solanacearum type III effector RipAC targets SGT1 to suppress effector-triggered immunity. Plant Cell Physiol. 61:2067-2076.


Nakano, M and Mukaihara, T 2019. The type III effector RipB from Ralstonia solanacearum RS1000 acts as a major avirulence factor in Nicotiana benthamiana and other Nicotiana species. Mol Plant Pathol. 20:1237-1251.



Parales, RE and Harwood, CS 1993. Construction and use of a new broad-host-range lacZ transcriptional fusion vector, pHRP309, for gram-bacteria. Gene. 133:23-30.


Parke, D 1990. Construction of mobilizable vectors derived from plasmids RP4, pUC18 and pUC19. Gene. 93:135-137.


Paul, MJ, Primavesi, LF, Jhurreea, D and Zhang, Y 2008. Trehalose metabolism and signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 59:417-441.


Peeters, N, Carrère, S, Anisimova, M, Plener, L, Cazalé, A-C and Genin, S 2013. Repertoire, unified nomenclature and evolution of the Type III effector gene set in the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex. BMC Genomics. 14:859.



Piazza, A, Zimaro, T, Garavaglia, BS, Ficarra, FA, Thomas, L, Marondedze, C, Feil, R, Lunn, JE, Gehring, C, Ottado, J and Gottig, N 2015. The dual nature of trehalose in citrus canker disease: a virulence factor for Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri and a trigger for plant defence responses. J Exp Bot. 66:2795-2811.



Poueymiro, M, Cazalé, AC, François, JM, Parrou, JL, Peeters, N and Genin, S 2014. A Ralstonia solanacearum type III effector directs the production of the plant signal metabolite trehalose-6-phosphate. mBio. 5:e02065-14.



Poueymiro, M, Cunnac, S, Barberis, P, Deslandes, L, Peeters, N, Cazale-Noel, A-C, Boucher, C and Genin, S 2009. Two type III secretion system effectors from Ralstonia solanacearum GMI1000 determine host-range specificity on tobacco. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 22:538-550.


Prior, P, Ailloud, F, Dalsing, BL, Remenant, B, Sanchez, B and Allen, C 2016. Genomic and proteomic evidence supporting the division of the plant pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum into three species. BMC Genomics. 17:90.



Safni, I, Cleenwerck, I, De Vos, P, Fegan, M, Sly, L and Kappler, U 2014. Polyphasic taxonomic revision of the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex: proposal to emend the descriptions of Ralstonia solanacearum and Ralstonia syzygii and reclassify current R. syzygii strains as Ralstonia syzygii subsp. syzygii subsp. nov., R. solanacearum phylotype IV strains as Ralstonia syzygii subsp. indonesiensis subsp. nov., banana blood disease bacterium strains as Ralstonia syzygii subsp. celebesensis subsp. nov. and R. solanacearum phylotype I and III strains as Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 64:3087-3103.


Schäfer, A, Tauch, A, Jäger, W, Kalinowski, J, Thierbach, G and Pühler, A 1994. Small mobilizable multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK18 and pK19: selection of defined deletions in the chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum
. Gene. 145:69-73.


Simon, R, Priefer, U and Pühler, A 1983. A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in gram negative bacteria. Bio/. Technology. 1:784-791.

Suga, Y, Horita, M, Umekita, M, Furuya, N and Tsuchiya, K 2013. Pathogenic characters of Japanese potato strains of Ralstonia solanacearum
. J Gen Plant Pathol. 79:110-114.

Sun, T, Wu, W, Wu, H, Rou, W, Zhou, Y, Zhuo, T, Fan, X, Hu, X and Zou, H 2020.
Ralstonia solanacearum elicitor RipX induces defense reaction by suppressing the mitochondrial atpA gene in host plant. Int J Mol Sci. 21:2000.



Tayeh, C, Randoux, B, Vincent, D, Bourdon, N and Reignault, P 2014. Exogenous trehalose induces defenses in wheat before and during a biotic stress caused by powdery mildew. Phytopathology. 104:293-305.


Tournu, H, Fiori, A and Van Dijck, P 2013. Relevance of trehalose in pathogenicity: some general rules, yet many exceptions. PLoS Pathog. 9:e1003447.



van Elsas, JD, Kastelein, P, de Vries, PM and van Overbeek, LS 2001. Effects of ecological factors on the survival and physiology of Ralstonia solanacearum bv. 2 in irrigation water. Can J Microbiol. 47:842-854.


- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 3,372 View
- 97 Download
- ORCID iDs
-
Yuki Ichinose

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7767-7912 - Related articles



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement
Supplement Print
Print



